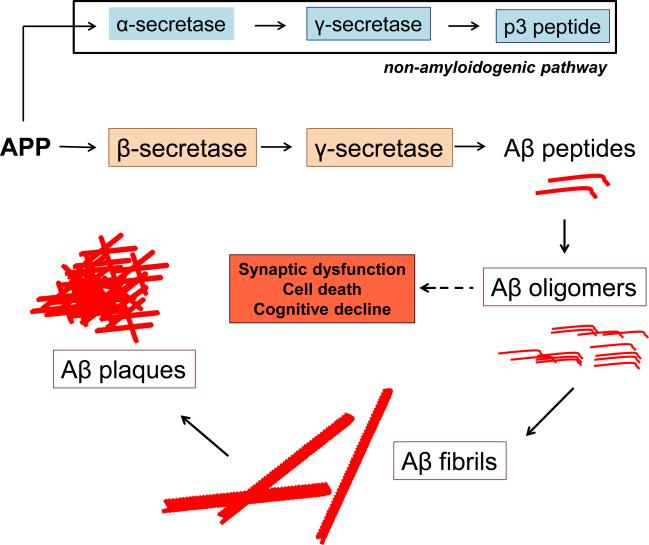
Figure 1. Aβ metabolic pathway.
The Aβ precursor protein (APP) is processed in one of two main pathways that yield either Aβ peptides or non-amyloidogenic products. If APP is sequentially cleaved by the α-secretase, and then, the γ-secretase, then nonamyloidogenic products form. However, if APP is cleaved by β-secretase and then γ-secretase, then Aβ is produced. As Aβ peptides continue to be produced, they form low-n oligomers, fibrils and eventually plaques. It is believed that soluble low-n oligomers produce the neuronal and cytotoxic injury in Alzheimer's disease.