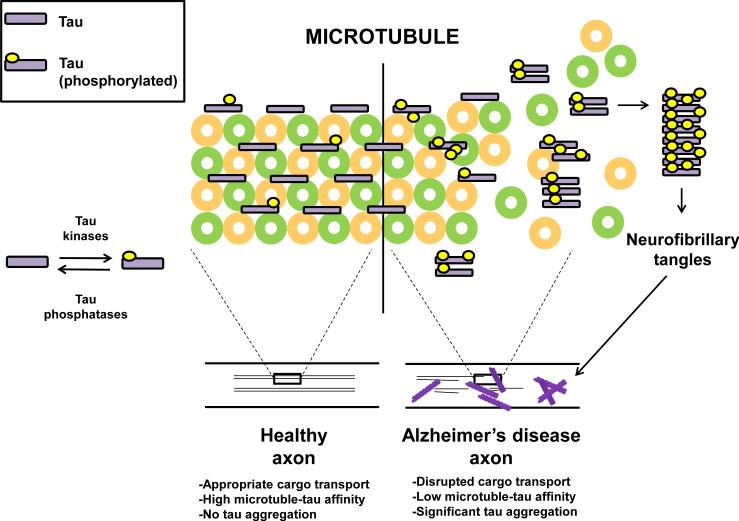
Figure 2. Tau metabolic pathway.
The microtubule-associated tau protein maintains phosphorylation status through the combined actions of tau-associated kinases and tau-associated phosphatases. When appropriate physiological tau phosphorylation is maintained, tau affinity to microtubules is maintained and microtubule structure, axon integrity and cellular function are preserved. When tau is hyperphosphorylated as found in Alzheimer's disease, tau is thought to lose affinity from microtubules, form insoluble aggregates, eventually leading to impaired axonal transport, neuronal ultrastructure damage and cell death.