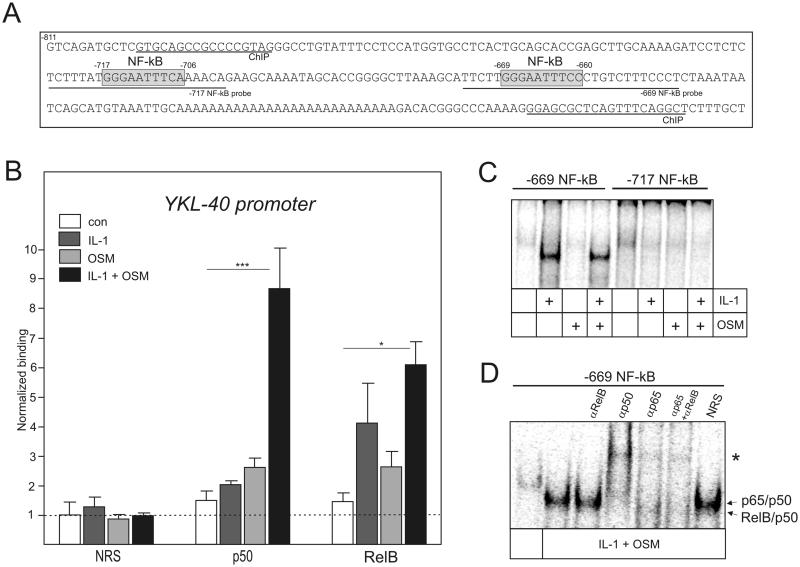
Fig. 5. RelB/p50 complexes bind at the distal NF-κB site of YKL-40 promoter.
(A) YKL-40 promoter. NF-κB sites are indicated by grey boxes. Positions of ChIP primers and probes used in EMSA (−717 and −669 probe) are indicated. (B) ChIP was performed using chromatin prepared from U373 cells treated with IL-1 and OSM for 2h. Binding of p50 and RelB to the YKL-40 promoter was analyzed using the antibodies described in the experimental procedures. NRS indicates normal rabbit serum used for immunoprecipitation. Results are shown as normalized binding (binding of NRS-immunoprecipitated untreated samples were set as 1). Experiments were performed three times. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA). (C-D) Nuclear extracts were prepared from U373 and glioma cells stimulated with IL-1 and OSM for 8 hours. The binding was then analyzed by EMSA using the 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes derived from the 5’ flanking region of the YKL-40 (−717 NF-kB and −669 NF-κB, as indicated). (C) Binding to the −717 NF-kB and −669 NF-κB elements in U373 glioma cells. (D) Binding to the −669 NF-kB probe in U373 cells. Specific antibodies or NRS were added to the binding reaction. Asterisk indicates super-shifted complexes.