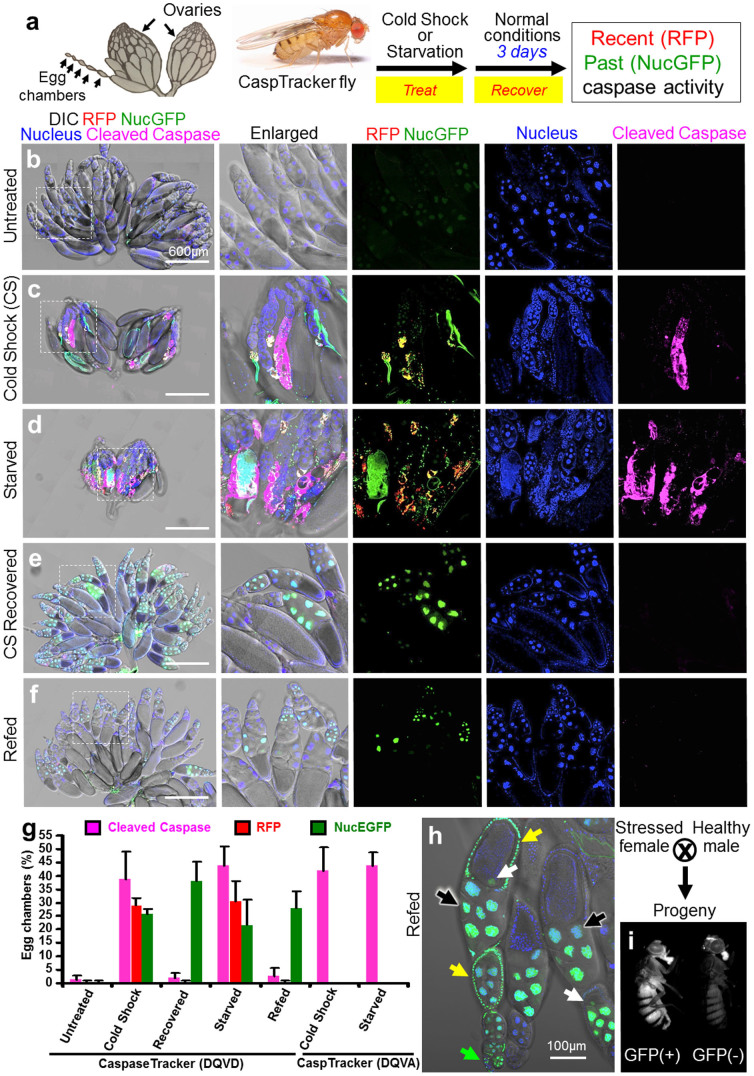
Figure 2. The CaspaseTracker System for detection of apoptosis and anastasis in vivo.
(a) Schematic of Drosophila ovary, and flow chart for cold shock-, and protein starvation-induced cell death in 1-day-old flies, followed by 3-days recovery at normal condition. Drosophila ovary drawing is provided by Polan Santos; Drosophila image is provided by Darren Obbard. Used with permission (b) Egg chambers from the ovary of 6-day female CaspaseTracker flies fed with normal fly food for 6 days (untreated). (c) Caspase biosensor activity in egg chambers of CaspaseTracker Drosophila at 1 day after cold shock (−7°C, 1 hour, followed by 25°C for 24 hours) to induce apoptosis in egg chambers. (d) Caspase biosensor activity in egg chambers of CaspaseTracker Drosophila fed 3 days with 8% sucrose in 1% agar (starved) to induce apoptosis in egg chambers. (e) Like panel c except flies were then switched to normal conditions for 3 days after cold shock (CS recovered). (f) Like panel d except flies were switched to normal yeast-based fly food for 3 days after starvation (refed). Panel at left most is merged confocal image of RFP, NucGFP, nuclei, cleaved-caspase immuno-staining and DIC for overview of egg chambers at the ovaries; middle left panel is enlarged view of the dotted box at the left most panel; middle, middle right, and right most panels display biosensor RFP and NucGFP, nucleus, and cleaved caspase, respectively. (g) Quantification of RFP and NucGFP expression in egg chambers of CaspaseTracker (DQVD) flies before and after apoptosis induction. Caspase insensitive CaspaseTracker (DQVA) files serve as controls. Data presented are from 3 different batches of flies (n = 20), counting 100 egg chambers from each batch per condition. Error bars denote SD. (h) Confocal image of egg chambers recovered 3 days after starvation. Nuclear GFP in nurse cells (black arrows), oocytes (white arrows) and follicle cells (yellow arrows) of egg chambers, and in the germarium (green arrow). (i) GFP and non-GFP expressing progeny from starved and refed CaspaseTracker (DQVD) female flies.