Figure 3. Schematic of fabrication process for 3D printing technique and the corresponding deformation of printed polymer described by a viscoelastic model.
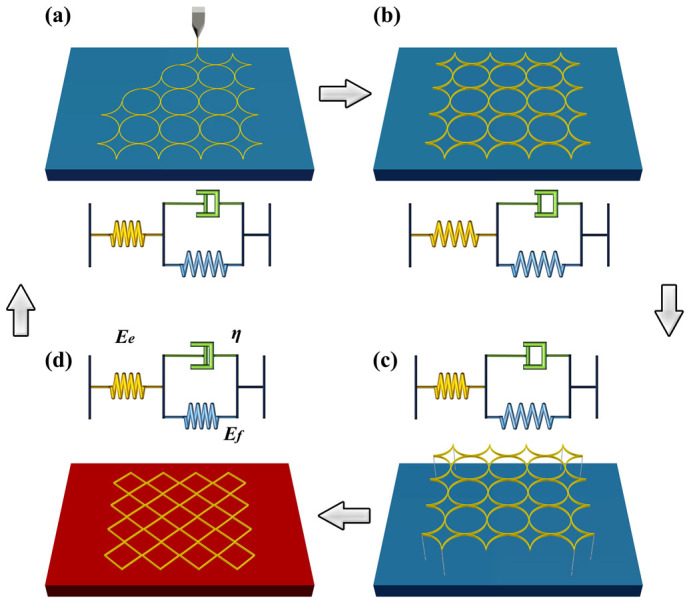
(a) The fused polymer is extruded from the nozzle and a constant strain is formed due to the moving of nozzle before it is bonded onto the platform of the 3D printer; (b) The printed polymer cools, solidifies, and bonds with platform or neighboring material and internal strain is generated during the process; (c) Removing the printed polymer from the platform leads to the recovery of elastic deformation, but an internal strain related to phase transition is stored in the printed polymer; (d) Internal strain stored in the polymer is released when reheated above its glass transition temperature, and can be explored to trigger pattern transformation of heat-shrinkable polymer.
