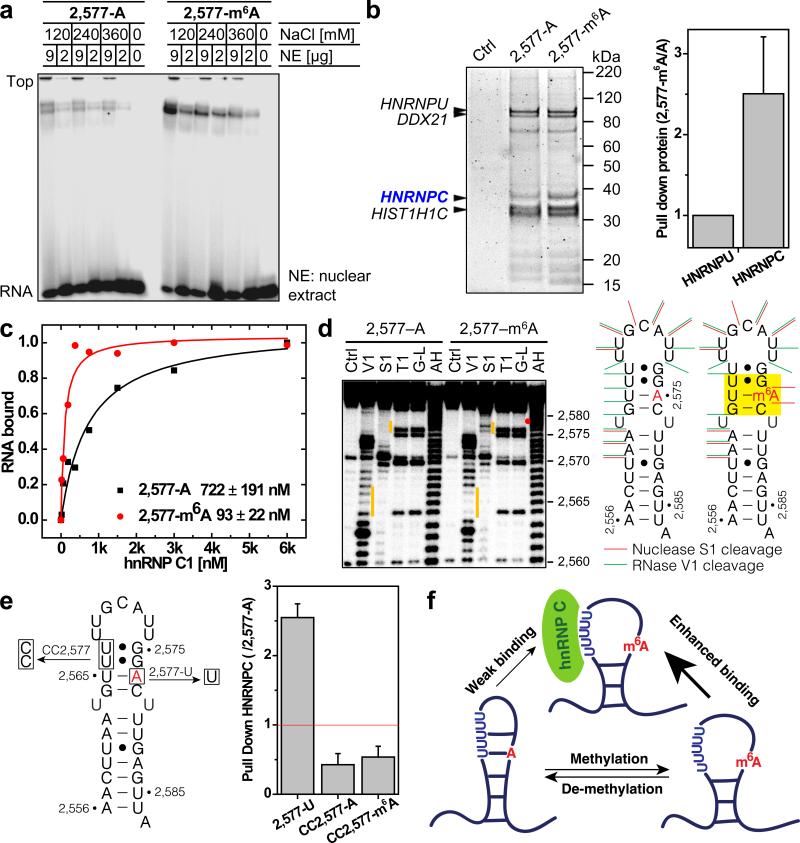
Figure 1. m6A alters RNA structure to enhance hnRNP C binding.
a, m6A increases binding with nuclear proteins. b, RNA pull down showing hnRNP C preferably binds methylated RNA. n = 4, ± s.d., biological replicates. c, Filter binding showing m6A increases hnRNP C1 binding with respective apparent dissociation constant (Kd) indicated at lower right; n = 3, ± s.d., technical replicates. d, RNA structural probing showing m6A disrupts local RNA structure highlighted in yellow. Ctrl, no nuclease added; V1, RNase V1 digestion; S1, nuclease S1 digestion; T1, RNase T1 digestion; G-L, G-ladder; AH, alkaline hydrolysis. The orange bars mark the structurally altered RNA regions in the presence of m6A (red dot). e, RNA pull down with mutated oligos. n = 3, ± s.d., technical replicates. f, Illustration of the m6A-switch model.