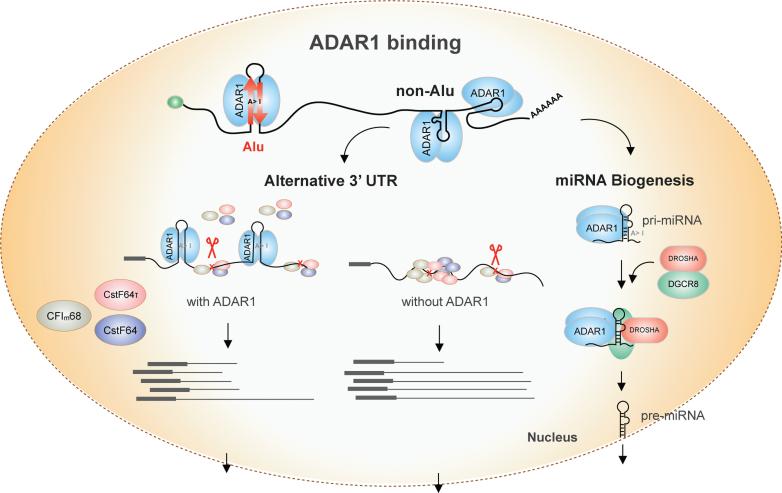
Figure 5. Schematic models of ADAR1 function in the nucleus on 3' UTR processing and miRNA biogenesis.
These regulatory mechanisms are mainly executed by ADAR1 binding to non-Alu regions. ADAR1 may compete with other cleavage and polyadenylation factors (CF Im68, CstF64 and CstF64τ) in binding to 3' UTRs. In the presence of ADAR1, the three proteins impose reduced regulatory influence on ADAR1-bound 3' UTRs than on other 3' UTRs. Upon ADAR1 KD, these proteins could gain more access to the 3' UTRs and exert regulation. The proximal cleavage site is often chosen in the presence of ADAR1, whereas the distal site is used upon ADAR1 KD. These outcomes reflect combinatorial regulation by the cleavage and polyadenylation factors that have opposing impacts on alternative 3' UTR usage. For pri-miRNA processing, ADAR1 may bind to (and edit) the nascent primary transcript prior to DROSHA/DGCR8 binding. The Microprocessor then cleaves the pri-miRNA with or without binding to the RNA. The binding of ADAR1 mainly promotes the processing of pri-miRNA, leading to enhanced miRNA expression level.