Figure 3.
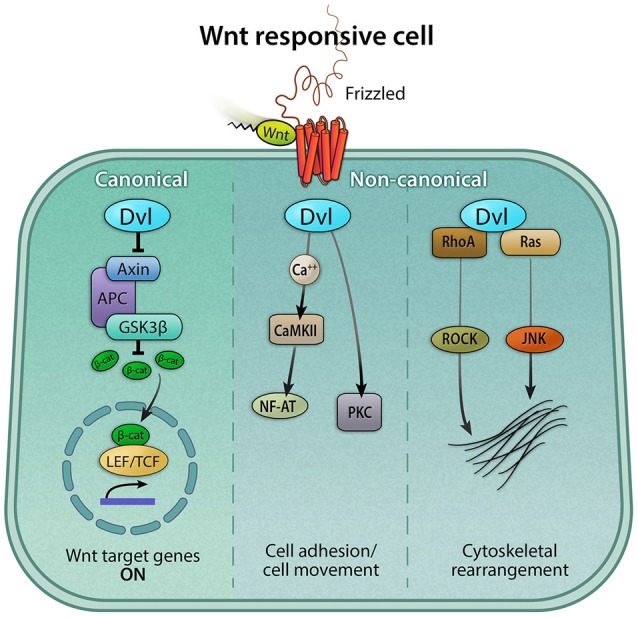
Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways. The Wnt pathway can be classified broadly as canonical and non-canonical. Both pathways are activated by a Wnt ligand to the Frizzled receptor. The active canonical pathway is mediated by β-catenin, which translocates into the nucleus and it acts as a co-activator of the TCF/LEF transcription factor, leading to the upregulation of Wnt target genes. The two major non-canonical pathways are Wnt/calcium and Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) pathways. In the Wnt/calcium pathway, Wnt binding to Frizzled activates Dvl, which stimulates calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum, activating calcium-binding proteins including protein kinase C (PKC) and calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII), and in turn, the transcription factor NFAT. The Wnt/calcium pathway has been shown to regulate cell movement and axis formation during embryogenesis. The Wnt/PCP pathway is mediated by the GTPases RhoA and Ras, which, via the activation of the RhoA-Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) axis or JNK, can exert effects on the cytoskeleton.
