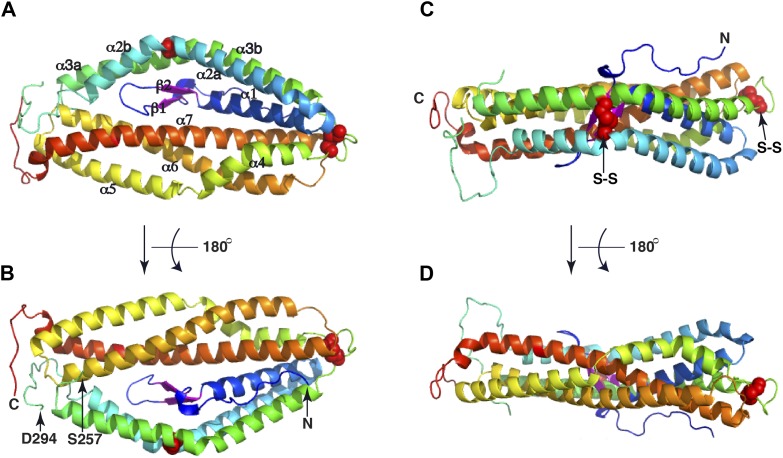
Figure 2. The crystal structure of PfRh5.
(A) Ribbon representation of the PfRh5 structure. Color scheme is rainbow (N-terminus: blue; C-terminus: red) except for the β-hairpin that is colored magenta for clarity. The cysteine residues that form disulfide bridges (Cys345–Cys351 and Cys224–Cys317) are shown as spheres. Helices α4, α5, α6, and α7 assemble as a triplet-helical coiled-coil domain running the length of the long axis of the molecule, helices α1, α2a, and α3b assemble to form a short triplet-helical bundle and helices α2b and α3a assemble to form a short two-helix coiled coil. (B) Ribbon representation of the PfRh5 structure viewed after a 180o rotation relative to that in (A). The residues between Ser257 and Asp294 are disordered. (C) Ribbon representation of the PfRh5 structure viewed from the side with the C-terminus on the left. The disulfide bridges are indicated with arrows. (D) Ribbon representation of the PfRh5 structure viewed after a 180o-rotation relative to that in (C).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04187.006
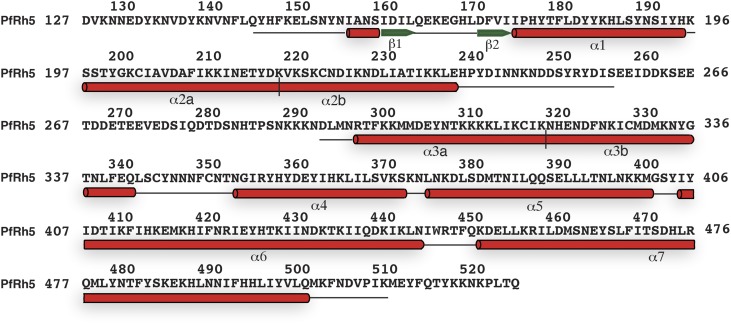
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. The secondary structure of PfRh5.
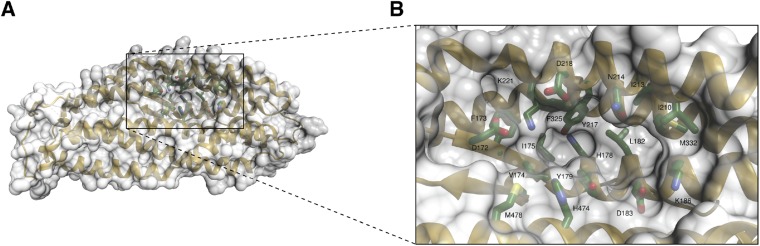
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Two free cysteine residues (Cys203 on α2a and Cys329 on α3b) within the crystal structure of PfRh5.
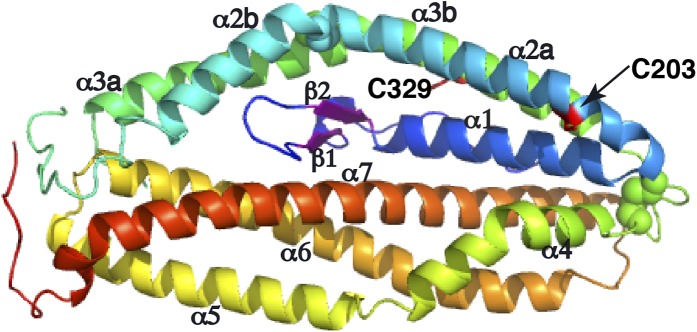
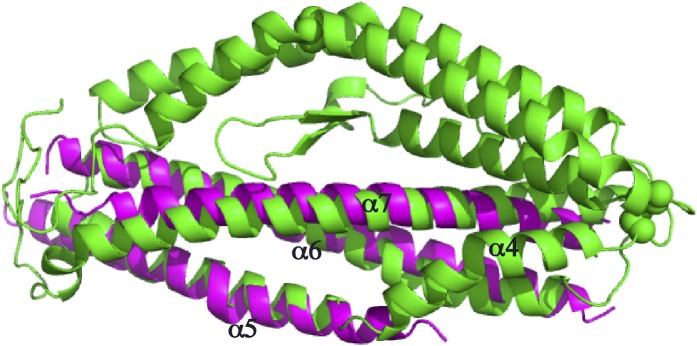
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Superimposition of the PfRh5 structure with N-terminal coiled-coil domain of SipB.