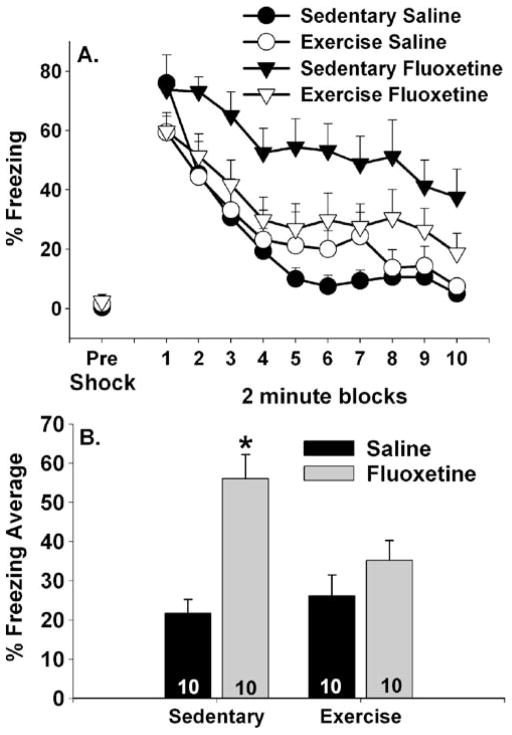
Fig. 7.
Effects of exercise on fluoxetine-induced exaggerated shock-elicited freezing. Rats remained sedentary or were allowed 6 weeks of voluntary access to running wheels prior to receiving a single injection of either saline or fluoxetine (10 mg/kg). Freezing behavior immediately before (pre-shock) and immediately following (representing fear conditioned to contextual or discrete cues in the shuttle box) three foot shocks was assessed in a shuttle box 1 h after fluoxetine injection. Data are presented as a 2-min blocks of freezing and b the mean percent shock-elicited freezing for the entire 20-min observation period. Data are means ± SEM. Asterisk p<0.05 relative to sedentary/ saline, exercised/saline, and exercised/fluoxetine groups. Group sizes are shown within the bars