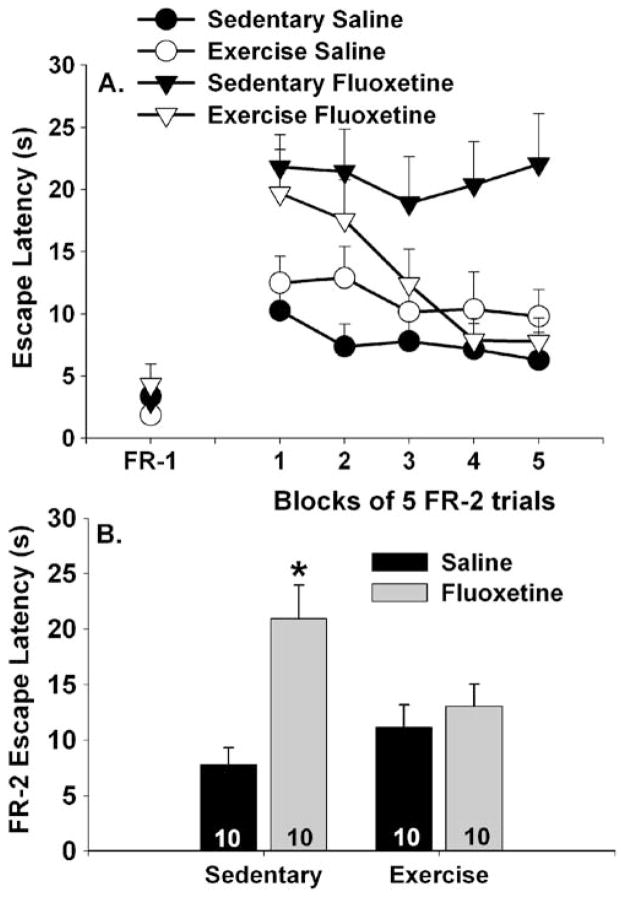
Fig. 8.
Effects of exercise on fluoxetine-induced escape deficit. Rats remained sedentary or were allowed 6 weeks of voluntary access to running wheels prior to receiving a single injection of either saline or fluoxetine (10 mg/kg). Rats were placed into shuttle boxes for assessment of fixed-ratio 1 (FR-1) and fixed-ratio 2 (FR-2) escape performance 1 h later. Data are presented as a blocks of five escape trials and b the mean escape latency for all 25 FR-2 escape trials. Data represent means ± SEM. Asterisk p<0.05 relative to sedentary/saline, exercised/saline, and exercised/fluoxetine groups. Numbers in each bar represent the number of rats included in that group