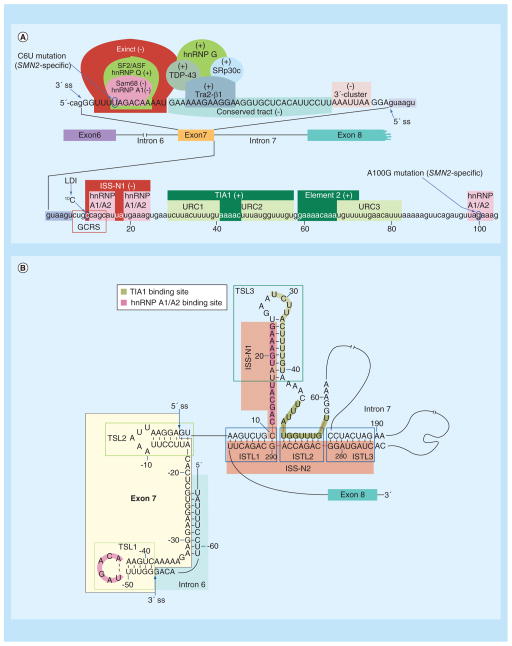
Figure 3. Regulators of SMN exon 7 splicing (see facing page).
(A) Diagrammatic representation of cis-elements and transacting factors that affect splicing of exon 7. Exon 7 sequence is shown in capital letters, while adjacent intronic sequences, including the first 104 nucleotides of intron 7, are shown in lower-case letters. The ss of exon 7 are indicated by arrows; in addition, the 5′ ss is highlighted with a blue arrow. Nucleotide numbering starts from the first position of intron 7. Cis-elements/transacting factors that promote exon 7 inclusion are indicated by (+), while cis-elements/transacting factors that promote exon 7 skipping are indicated by (−). Exinct, the conserved tract and 3′-Cluster were identified by in vivo selection of the entire exon 7 [89]. Element 2 and binding sites for hnRNP A1/A2, Sam68, SF2/ASF, hnRNP Q, Tra2-β1, TDP-43, hnRNP G and SRp30c were described previously [88,90]. TIA1 binds to URC1 and URC2 located in intron 7 and promotes exon 7 inclusion [90]. ISS-N1, along with the overlapping GCRS and the 10C, which is involved in LDI, contribute to skipping of exon 7 [90]. TSL2 structure sequesters the 5′ ss of exon 7 and promotes its skipping [91]. The presentation is adapted from [92]. (B) Schematic representation of the partial RNA secondary structure formed by the sequences that constitute SMN2 exon 7, the last 14 nucleotides of intron 6 and the entire intron 7. The structure is based on the results of chemical structure probing performed in [91,92]. Arrows indicate the 5′ and 3′ ss of exon 7. Exon 7 and intron 6 sequences are highlighted in yellow and light blue, respectively. Nucleotide numbering starts from the first position of intron 7. Three TSLs are marked by green boxes. The juxtaposed internal stems formed by LDI (ISTLs) are marked by blue boxes. ISS-N1 and ISS-N2 are highlighted in red. The adjacent 3′-strands of ISTL1, ISTL2 and ISTL3 constitute ISS-N2. Binding sites of TIA1 and hnRNP A1/A2 are indicated.
GCRS: GC-rich sequence; ISS-N1: Intronic splicing silencer N1; LDI: Long-distance interaction; ss: Splice site; TSL: Terminal stem-loop; URC: U-rich cluster.