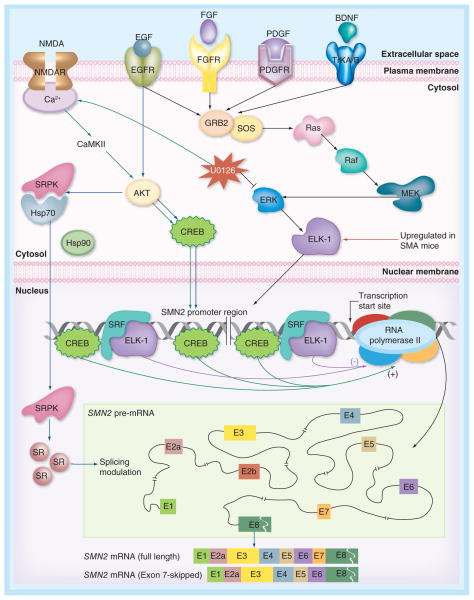
Figure 5. Signaling pathways implicated in regulation of SMN2 transcription and SMN2 exon 7 splicing.
Simplified version of intracellular MEK/ERK and AKT/CREB signaling pathways that affect SMN transcription, including the upstream regulators (NMDA, EGF, FGF, PDGF and BDNF). Activation of spinal cord NMDA receptors or inhibition of ERK by U0126 activates the AKT pathway leading to increased SMN2 transcription [118,120]. Activation of AKT triggers autophosphorylation of SRPK followed by its nuclear import and consequent phosphorylation of SR proteins that regulate alternative splicing [124]. Binding sites of transcription factors within SMN2 promoter are shown. In the inset for SMN2 pre-mRNA, exonic (coding) and intronic (non-coding) regions are indicated by boxes and lines, respectively. Two major SMN2 splice isoforms are shown at the bottom.
EGFR: EGF receptor; FGFR: FGF receptor; NMDAR: NMDA receptor; PDGFR: PDGF receptor.