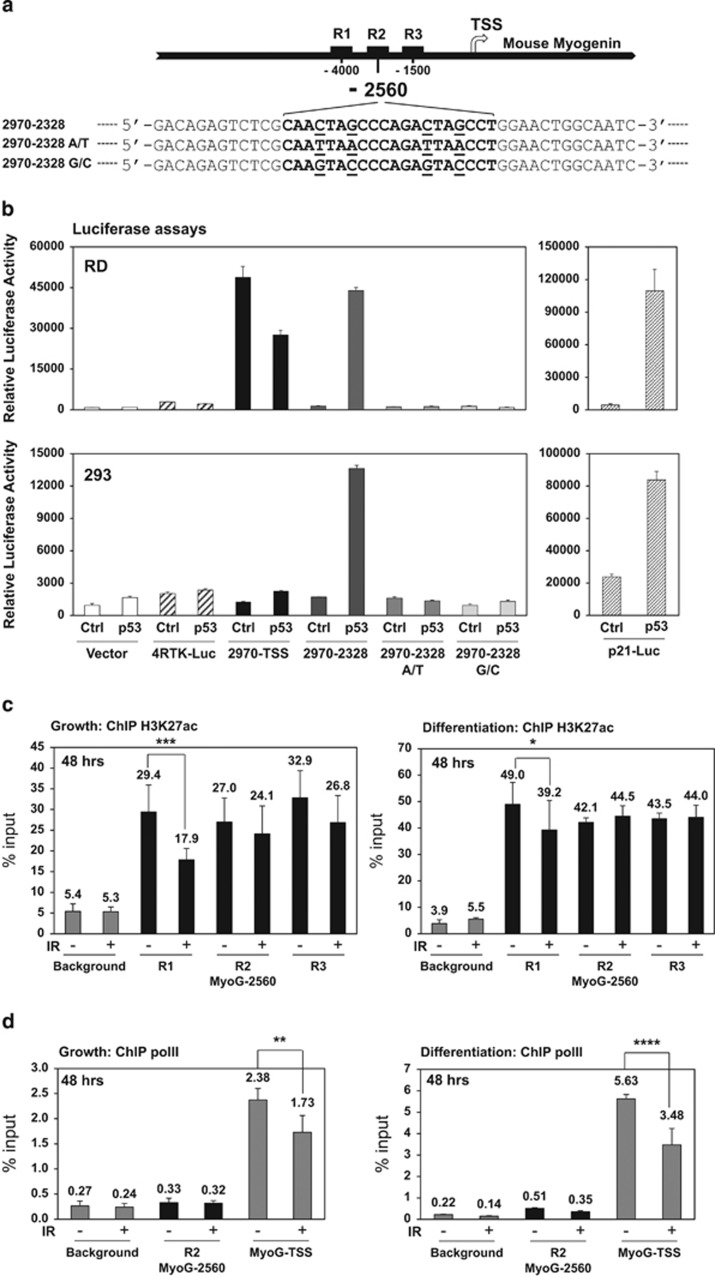
Figure 4.
Repression of myogenin by p53 is partially mediated through a distal enhancer region upstream of the mouse myogenin gene. (a) Schematics of the distal enhancer region upstream of the mouse myogenin gene. Black squares: R1, R2, and R3 enhancer elements; arrow: transcription start site (TSS). The p53 consensus binding sequence is characterized as two half sites of RRRCWWGYYY (R=purine, W=adenine or thymine, and Y=pyrimidine) with a spacer of 0–13 base pairs between each half site.43 Mouse myogenin p53 RE at−2560 site is shown in the bracket and mutations at the consensus sites are underlined as 2970–2328 A/T or G/C. (b) p53-ER transcriptional activity at 24 h of 4OHT induction was validated by luciferase reporter assays in RD or 293 cells. The reporter 2970-TSS includes the fragment from −2970 to TSS. The reporter 2970-2328 includes the fragment from −2970 to −2328. pGL3 vector and 4RTK-Luc served as negative controls. p21-Luc served as a positive control. (c) ChIP analysis of histone H3K27ac enrichment to mouse myogenin enhancer elements at 48 h post IR in C2C12 myoblasts maintained under either growth or differentiation condition. ChIP background was measured by binding of the H3K27ac antibody to a gene desert region. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. (d) ChIP analysis of polymerase II enrichment to mouse myogenin R2 (MyoG-2560) and TSS at 48 h post IR in C2C12 myoblasts maintained under either growth or differentiation condition. ChIP background was measured by binding of the polymerase II antibody to a gene desert region. **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001