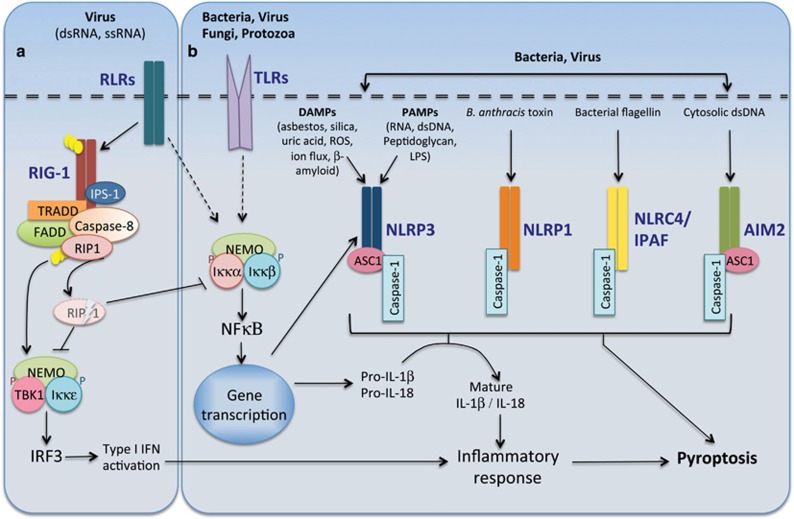
Figure 3.
Caspase-mediated inflammatory responses. (a) Caspase-8 functions to restrict RIG-1 signaling. Activation of the retinoic-acid-like receptors (RLRs) are critical for anti-viral immunity. Following viral infection the caspase-8 DISC complex comprising FADD, TRADD and ubiquitin-conjugated RIP1 (Ub-RIP1) are recruited to the RIG-1 complex. Although Ub-RIP1 can enhance the phosphorylation of IRF3, it is also cleaved by activated caspase-8. Cleaved RIP1 inhibits IRF3 and NFκB thereby reducing the type I interferon (IFN) and IL-1β-/IL-18-mediated inflammatory responses. (b) Inflammasome complex formation is triggered by specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) following pathogen exposure induces NFκB-mediated transcription of IL-1β, IL-18 and also NLRP3, and this is an important step in inflammasome priming and activation. Caspase-1 activation is mediated by its recruitment to different inflammasome complexes (NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4 and AIM2) in an ASC-dependent or independent manner. Activated caspase-1 mediates the cleavage and maturation of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18. Following acute infection and an acute inflammatory response, caspase-1 induces cell death by pyroptosis