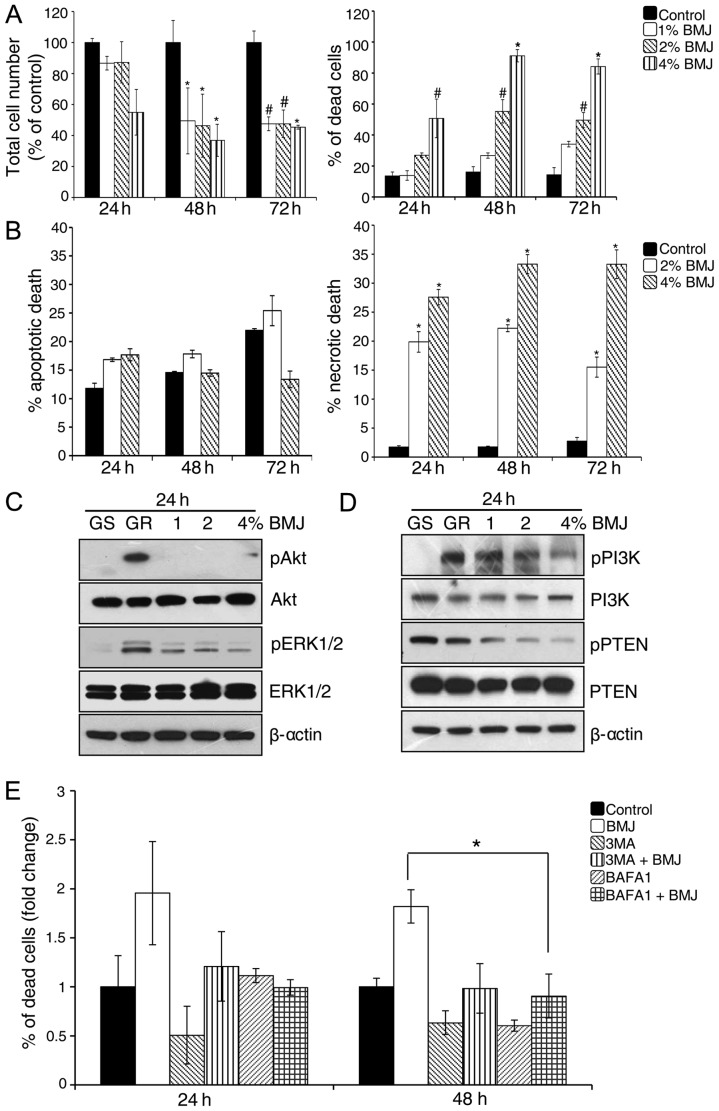
Figure 5.
Bitter melon juice (BMJ) inhibits the viability of gemcitabine-resistant (GR) AsPC-1 cells via targeting PI3K/Akt signaling, which is autophagy-dependent. (A and B) GR AsPC-1 cells were treated with 1–4% BMJ (v/v) for 24–72 h. At the end of each time point, both adherent and non-adherent cells were collected and processed for the determination of total cell number and dead cell percentage, or percentage of apoptotic and necrotic cell death following procedures in Materials and methods. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of three samples. *P≤0.001, #p≤0.01. (C and D) GR AsPC-1 cells were treated with 1–4% BMJ (v/v), total cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by western blotting for phosphorylated and total Akt, ERK1/2, PI3K and PTEN. Protein loading was confirmed by re-probing the membrane with β-actin antibody. Gemcitabine-sensitive (GS) AsPC-1 cells served as relevant control in this experiment. (E) GR AsPC-1 cells were pre-treated with early autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) or late autophagy inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (BAFA1) with or without BMJ (4%) treatment for 24 and 48 h, and dead cell percentage in each group was measured by trypan blue assay. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of three samples. *P≤0.001.