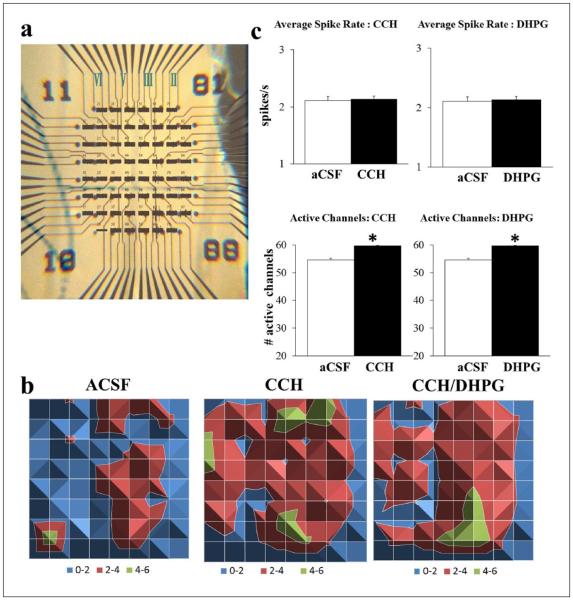
Figure 1.
CCH (20 μM) and DHPG (100 μM) induced recruitment of neuronal activity. (a) Example mPFC slice overlaid on recording channels marked for prelimbic (PL; top), infralimbic (IL; bottom) and layers II–VI (right to left) using a graticule scale. (b) Surface maps display the average spike rate per channel in 1 min (colour-coded legend) spreading from layer II/III to layer V/VI following CCH. When combined with DHPG (n = 25), there was a similar increase in the number of active channels and a reduction in spike rate per channel without a change in the total spike rate compared to CCH alone. (c) Either CCH (left; n = 80) or DHPG (right; n = 55) on its own did not affect total spike rate (top) but increased the number of active channels (bottom; *p < 0.05; open: control aCSF; filled: drug).