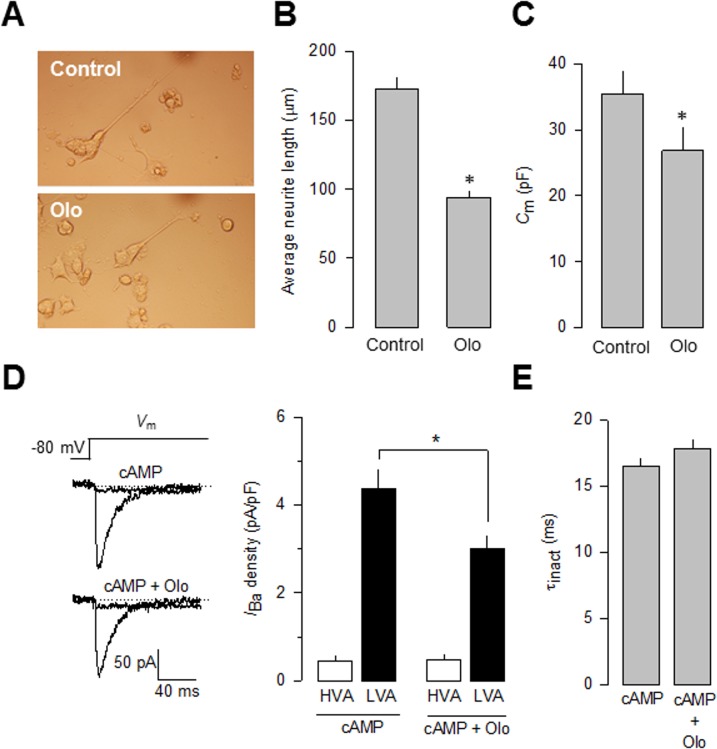
Fig 3. Cdk5 inhibits T-type Ca2+ channel functional expression and affect cAMP-mediated N1E-115 cell differentiation.
A) Inhibition of neurite outgrowth by the specific Cdk5 inhibitor olomoucine (Olo) in N1E-115 differentiated with cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, 2 mM) for 48 h. Phase contrast micrographs of cells grown in the absence or presence of Olo (50 μM). B) Comparison of neurite outgrowth from N1E-115 cells kept in culture in the absence (control) and presence of Olo. Neurite analysis was carried out with ImageJ software (NIH). C) Comparison of the C m values in cAMP-differentiated N1E-115 cells kept in culture in the presence or the absence of Olo. D) Representative superimposed trace currents recorded in response to 1 s depolarizing pulses to −30 mV from a V h of −80 mV (to evoke LVA channel activity), and to +10 mV at the end of the 1 s LVA current inactivating pulses (to evoke the HVA component of the current) in cAMP-differentiated N1E-115 cells in the presence or the absence of Olo (left panel). Comparison of the percentage of peak current densities through HVA and LVA channels (right panel). Data are given as mean ± S.E.M. E) Comparison of the time constant of current and inactivation (τinact) at −30 mV in cAMP-differentiated N1E-115 cells in the presence or the absence of Olo as in D.