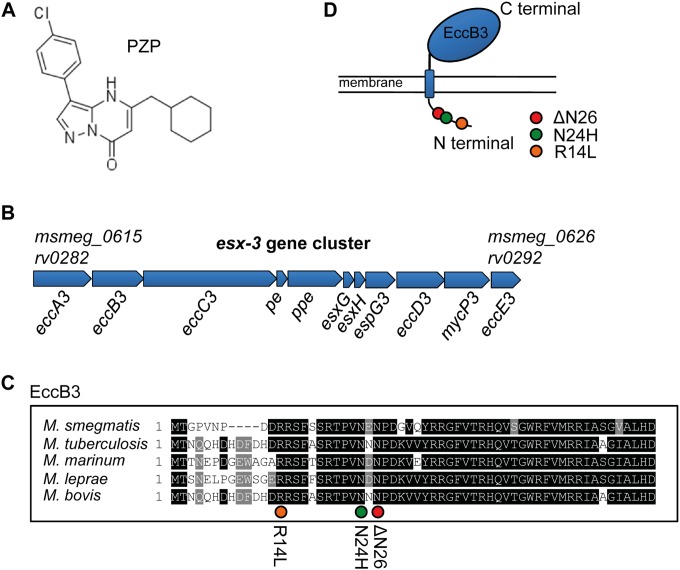
FIG 1.
Clones of M. tuberculosis resistant to PZP have mutations in the eccB3 gene of ESX-3. (A) Chemical structure of PZP. (B) The esx-3 gene cluster is composed of 11 genes stretching from MSMEG_0615 to MSMEG_0626 in M. smegmatis (SmegmaList, http://mycobrowser.epfl.ch/smegmalist.html) and rv0282 to rv0292 in M. tuberculosis (TubercuList, http://tuberculist.epfl.ch/index.html). (C) Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal end of EccB3. Black highlighting indicates conserved residues in mycobacteria. Orange, green, and red circles indicate the locations of mutated residues in PZP-resistant M. tuberculosis (R14L, N24H, and ΔN26 mutations). (D) EccB3 is a transmembrane protein with a predicted small (the first 71 amino acids) cytosolic tail on the N terminus and a large (amino acid 95 to 538) extracellular C-terminal domain. The mutations R14L, N24H, and ΔN26 are localized to the cytosolic tail, as indicated.