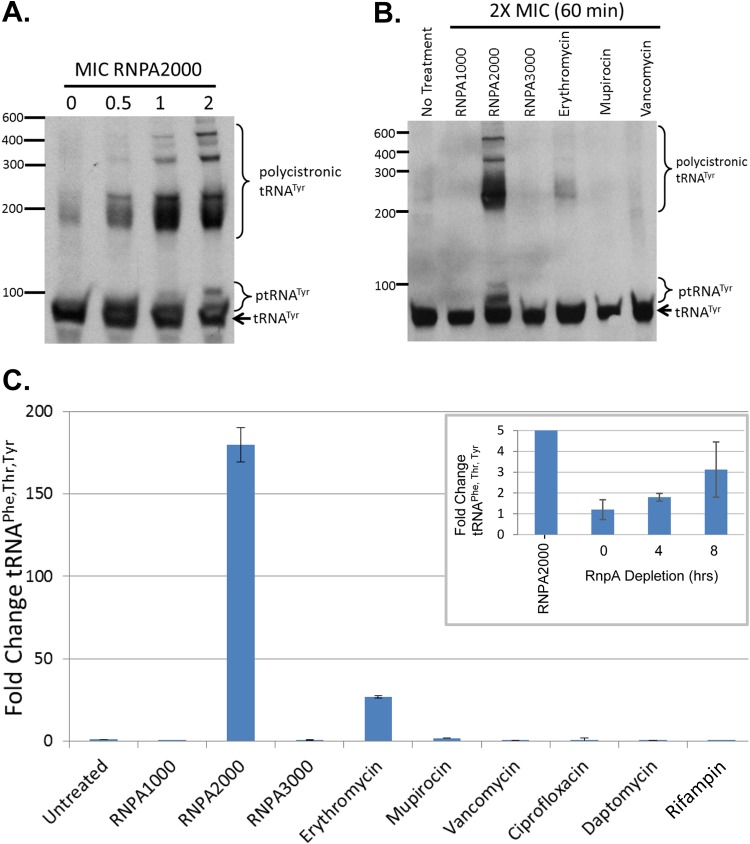
FIG 5.
RNPA2000 treatment leads to ptRNATyr and polycistronic tRNATyr accumulation within S. aureus cells. (A) Northern blotting results for S. aureus tRNATyr following treatment with increasing concentrations of RNPA2000 (0×, 0.5×, 1×, and 2× the MIC). (B) Northern blotting results probing for tRNATyr species within S. aureus treated with the putative RnpA inhibitors RNPA1000, RNPA2000, and RNPA3000, as well as antibiotics affecting other cellular targets. (C) qRT-PCR-based quantification of polycistronic tRNAPhe, Thr, Tyr levels within S. aureus cells treated with 2× the MIC of RNPA1000, RNPA2000, RNPA3000, or the indicated RnpA-independent antibiotic. Levels of tRNAPhe, Thr, Tyr within RnpA depletion cells (pML100:: A.S.-rnpA; rnpA mRNA-directed antisense molecule) cultured for the indicated time under low-induction conditions (5 ng ml−1 ATc, inset) relative to vector-containing cells; RNPA2000-treated cells are also shown (160-fold increase relative to mock-treated S. aureus cells).