Figure 6.
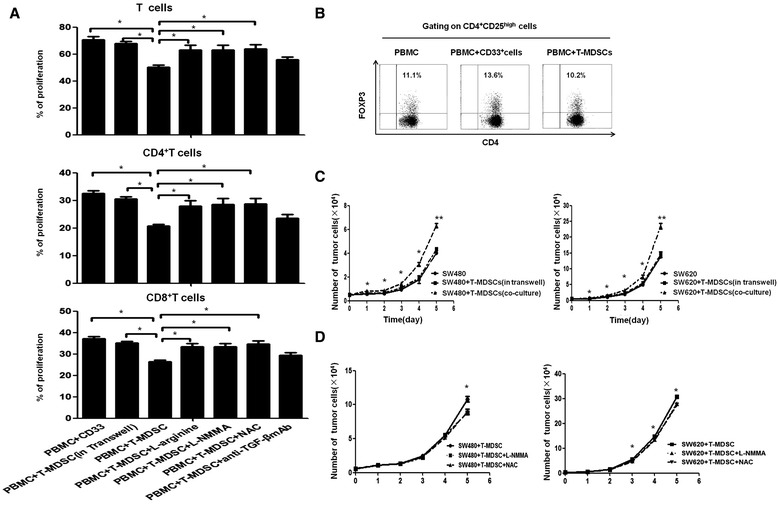
The mechanisms of the immunological and non-immunological functions of tumor-induced MDSCs. (A) The inhibition of T cell proliferation by tumor-induced MDSCs was rescued by a Transwell insert (put MDSC in inner well and PBMC in outer well) and inhibitors of L-Arg, iNOS and ROS, but not by anti-TGF-β. The statistical graph shows the mean value of 5 experiments. *P < 0.05. (B) CD4+ T cells were co-cultured with T-MDSC and CD33+ cells or in IL-2 medium alone in an OKT-3 stimulated 48-well cell plate for 3 days and then stained with anti-CD4, anti-CD25, and anti-FOXP3. The cells were analyzed using flow cytometry. One representative dot plot of three experiments is shown. (C) The tumor-induced MDSCs promoted the growth of SW480 and SW620 cells via a cell-to-cell contact-dependent mechanism. The cells were seeded into a 96 or 48-well plate at 5 × 103cells/well and were co-cultured with T-MDSCs at a 1:1 ratio or were co-cultured with T-MDSCs in a Transwell system for 5 days. The number of SW480 or SW620 cells was significantly increased after co-culture with T-MDSCs compared with the number of SW480 or SW620 cells cultured in medium alone or with the number of SW480 or SW620 cells after co-culture with T-MDSCs in the Transwell system. (D) The promotion of CRC tumor-induced MDSCs on the growth of SW480 and SW620 cells was significantly decreased by the inhibitors of ROS and iNOS. The error bars represent the SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
