Figure 3.
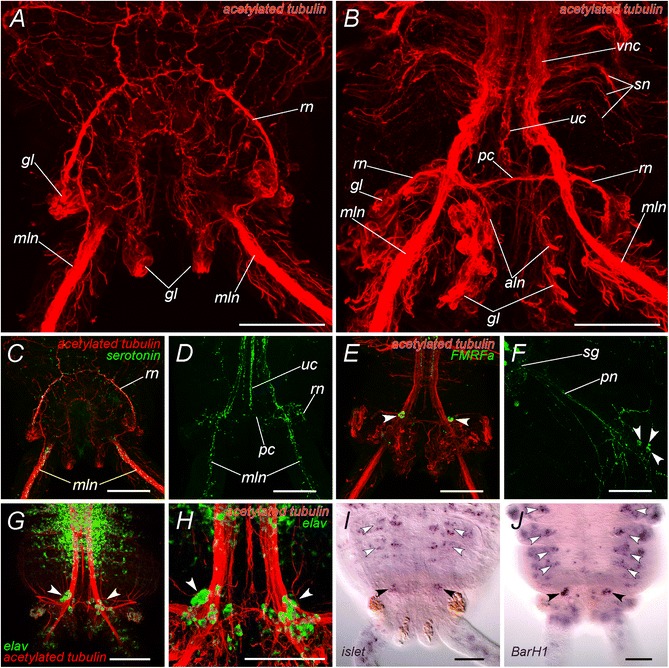
Molecular characterization of the nervous system of atokous P. dumerilii pygidium. A-B: Confocal micrographs showing acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity. C-D: Serotonin-positive (green) and acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity (red, C only). E-F: FMRFamide-like (green) and acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity (red, E only) in pygidium (E) and the peripheral nerves of a mid-body parapodium (F). G-H: elav-positive cells in the pygidium (green); nerves are counterstained with acetylated α-tubulin antibodies (red). I: Pdu-Islet expression in the pygidium and nascent segments. J: Pdu-BarH1 expression in the pygidium and nascent segments. View from the dorsal (A, C) and from the ventral (B, D-J) sides. sn - developping segmental nerves; vnc - ventral nerve cord; uc - unpaired nerve of the ventral nerve cord; rn - pygidial ring nerve; pc - pygidial commissure; mln - main longitudinal nerve; aln - additional pygidial longitudinal nerves; gl - pygidial glands; pn - parapodial nerve. Arrowheads show FMRFamide-like immunoreactive cells (E, F) and elav-positive cells (G, H).Black arrowheads and white arrowheads show Islet- (I) and BarH1- (J) positive cells in the pygidium and in cells of the parapodial ganglia, respectively. Scale bar 50 μm.
