Fig. 5.
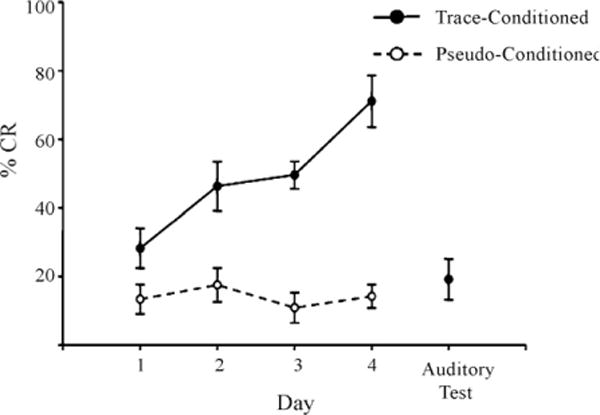
Using the described whisker stimulator to deflect whiskers as a conditioned stimulus, mice were able to learn forebrain-dependent, trace eyeblink conditioning. The percent number of conditioned responses (%CR) across the four days of training significantly increased for the trace-conditioned (filled circles, solid line) compared to the pseudo-conditioned mice (open circles, dotted line; F(3,33) = 7.09; p< 0.001). For the last day of training (Auditory Test) the comb was detached from the whisker stimulator and the trace-conditioned mice were given one additional day of training. Note the drop in performance to pseudo-conditioned levels during the auditory test indicating that the mice utilized whisker stimulation to learn the association. Error bars = standard error of the mean.
