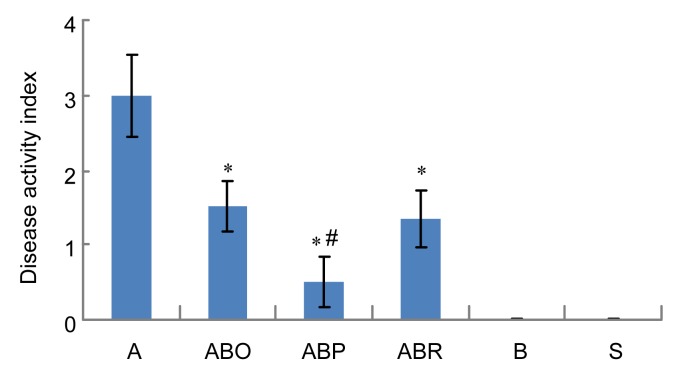
Fig. 2.
Effect of sodium butyrate administration on acetic acid (AA) colitis disease activity index
Rats were treated intrarectally with 4% acetic acid alone (A) or after 7 consecutive days of treatment with 100 mg/kg sodium butyrate orally (ABO), intrarectally (ABR) or intraperitoneally (ABP). Values for control rats receiving butyrate alone (B) or physiological saline (S) are also indicated. Disease activity index is obtained by combining scores of weight loss, stool consistency, and bleeding divided by 3. Results are expressed as mean±SEM (n=8). * Significantly different from AA colitis group at P<0.05. # Significantly different from another route of butyrate administration at P<0.05