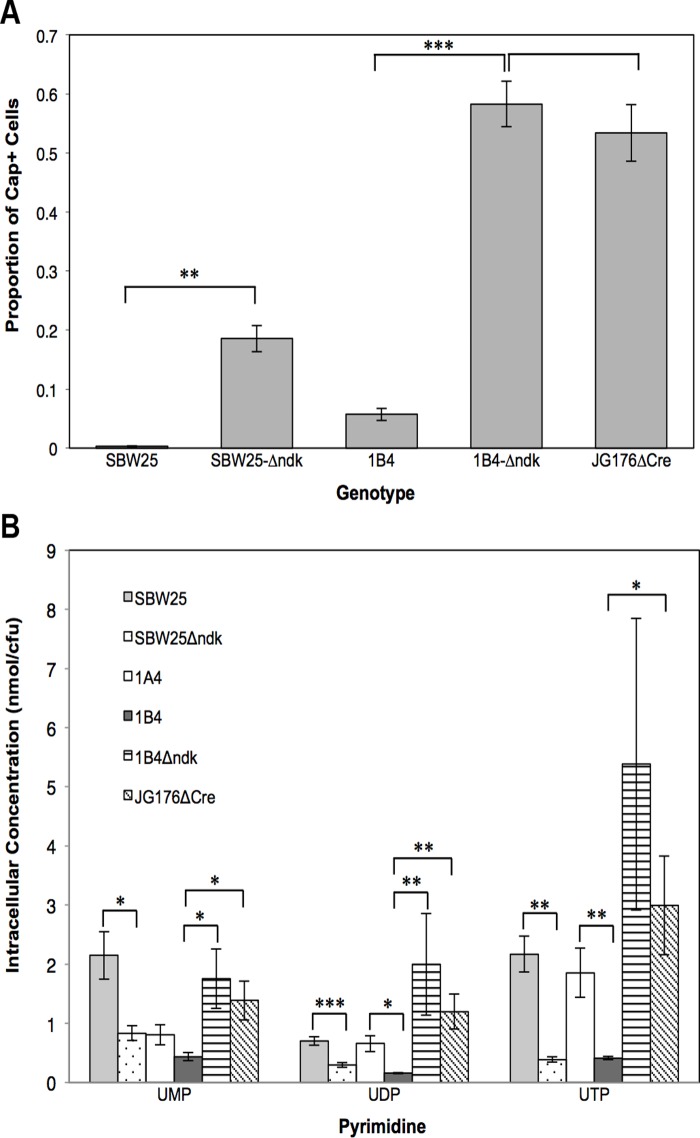
Fig 4. Deleterious mutations in carB and ndk affect capsulation and intracellular concentrations of pyrimidine intermediates.
The ndk gene was deleted from SBW25 and 1B4 using genetic engineering techniques, giving SBW25-Δndk and 1B4-Δndk, and the effects on capsule switching and pyrimidine pathway intermediates were determined. Bars are means of five replicates, and error bars show +/- 1 SE. (A) Capsulation levels in evolved and engineered genotypes. Deletion of ndk caused an increase in capsulation in SBW25 (i.e., in the absence of a carB mutation; Wilcoxon rank-sum test p < 0.01) and 1B4 (i.e., in the presence of c2020t carB; Welch two-sample t test; p < 0.001). No significant difference in capsulation levels was found between 1B4-Δndk and the ndk transposon mutant, JG176ΔCre (two-sample t test, p > 0.5). (B) Uridine monophosphate (UMP), UDP, and UTP levels were measured in the indicated genotypes (see S7 Table and S8 Table for independent measurements and measurement of additional metabolites and genotypes). The c2020t carB mutation significantly reduced concentrations of UDP and UTP (two-sample t tests for 1A4 versus 1B4, p < 0.05). Similarly, deletion of ndk significantly reduced concentrations of UMP, UDP, and UTP (two-sample t tests for SBW25 versus SBW25-Δndk, p < 0.05). Coexistence of c2020t carB and the ndk deletion resulted in an increase in UMP, UDP, and UTP (two-sample t tests or Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for 1B4 versus 1B4-Δndk and/or JG176ΔCre, p < 0.05). No significant differences in UMP, UDP, or UTP concentrations were found between 1B4-Δndk and the ndk transposon mutant, JG176ΔCre (two-sample t tests or Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, p > 0.05).