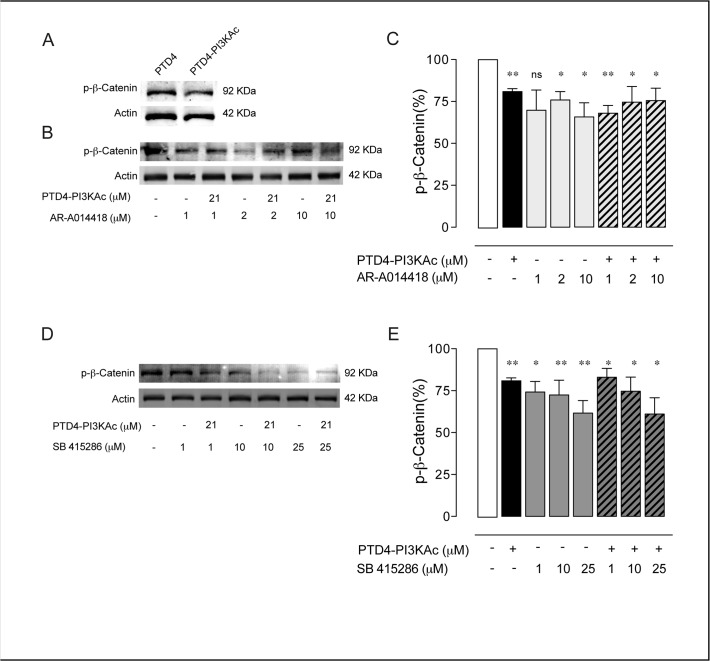
Fig 5. GSK3 inhibition results in a decrease of p-β-Catenin.
A. Immunoblot of p-β-Catenin from 12 DIV hippocampal neurons treated for 48 hours with PTD4-PI3KAc or PTD4 (21 μM). B. Immunoblot of p-β-Catenin after AR-A014418 treatment, alone or in combination with PTD4-PI3KAc (21 μM). Phosphorylation levels were normalized to the total actin. C. Plot bar representing the mean average of p-β-Catenin after the described treatment. All percentages are referred to control conditions as 100%, always included in each Western-blot membrane. Only the treatment with 2 and 10 μM of AR-A014418 decreased p-β-Catenin levels. The co-treatment with the PI3K activator did not induce a further reduction. D. Immunoblot of p-β-Catenin after SB 415286 or in combination with PTD4-PI3KAc (21 μM) treatments. E. Plot bar of the percentage of p-β-Catenin after treatment with SB 415286. Exposure of cells to SB 415286 or in combination with PI3K activator led to a statistically significant decrease in p-β-Catenin (n = 15 from 15 different cultures). Percentage of p-β-Catenin was normalized to the total Actin levels. Significance refers to the statistical analysis of the experiments versus the control (100%). Student’s two-tailed t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.005.