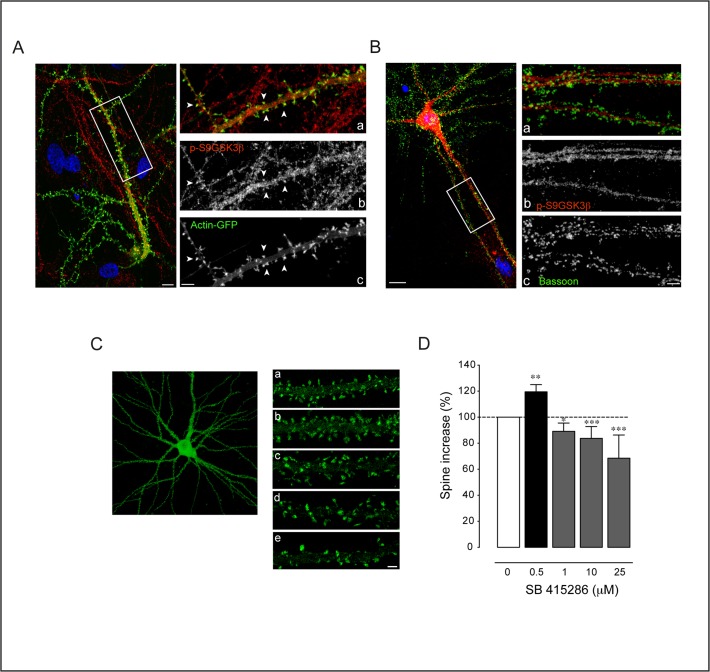
Fig 9. Localization of p-S9GSK3β at the synapse and spine effects of its inhibition.
A. p-S9GSK3β localizes at the postsynaptic side. Left: Single confocal microscopy image of a GFP-Actin transfected neuron counterstained with p-S9GSK3β in red and nuclei in blue (DAPI). Note that the cell body of the transfected neuron is not in the same focal plane (bottom right corner of the image). Scale bar = 5 μm. Right: High magnification view of the area depicted in the white box showing the (a) Merged picture of (b) p-S9GSK3β in red and (c) Actin-GFP signals in green. Positive spines for p-S9GSK3β are indicated by white arrowheads. Scale bars = 3 μm. B. p-S9GSK3β does not colocalize with presynaptic Bassoon. Left: 21 DIV old hippocampal neuron stained with p-S9GSK3β in red, Bassoon in green and nuclei in blue (DAPI). Scale bar = 5 μm. Right panels: high magnification view of the area depicted in the white box showing (a) Merged picture of (b) p-S9GSK3β in red and (c) Bassoon in green. Notice the total absence of colocalization between both markers. Scale bar = 3 μm. C. GSK3 inhibition has a differential effect on spine density. Actin-GFP transfected neurons of 19 DIV were treated for 48 hours with different concentrations of SB 415286. a, b, c, d, e, Dendritic fragments of a control (top), 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM and 25 μM of SB 415286 treated neurons, respectively. D. Plot graph summary of the effects on spine density [number of cultures: n = 3 (0.5 μM); n = 4 (1 μM); n = 3 (10 μM); n = 2 (25 μM)]. Average number of spines were compared and normalized in front of control cultures. Student’s two-tailed t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0001.