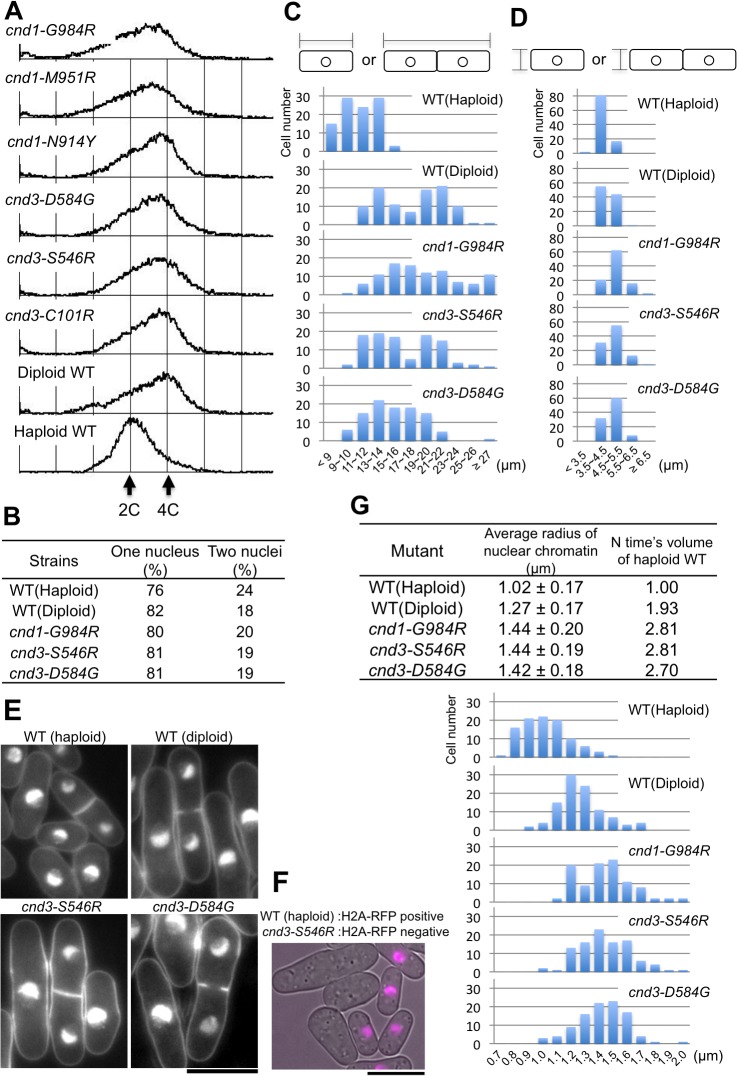
Fig 7. Damage-sensitive, non-SMC mutants are impaired in ploidy maintenance.
A. FACS data of wild type (haploid, diploid), and six mutants. See text. B. The number of nuclei per cell in the wild-type (haploid, diploid) and three mutant cells. About 80% of all cells contained a single nucleus, while the remaining 20% contained two nuclei with or without the septum. The latter cells represent those after nuclear division and prior to cytokinesis in the cell division cycle. See top figures in C. C. Cell length distributions of wild type (haploid, diploid), and three non-SMC cnd mutants. Diploid cells and mutant cells are longer than haploid cells. D. Cell width measurements of wild types (haploid and diploid) and mutant cells. E. Micrographs of wild types (haploid and diploid) and two mutant cells stained with DAPI are shown. The bar indicates 10 μm. F. Equal numbers of histone H2A-RFP haploid wild-type cells and cnd3-S546R mutant cells from liquid cultures were mixed together for microscopy. All small cells are RFP positive, while large cells are RFP negative. The bar indicates 10 μm. G. Average nuclear radius (with standard deviations) was measured for wild type (haploid, diploid), and three mutant cells. Three mutant nuclei were clearly larger than that of the wild-type haploid. The top panel indicates the average length. The bottom panel shows distributions of nuclear radii.