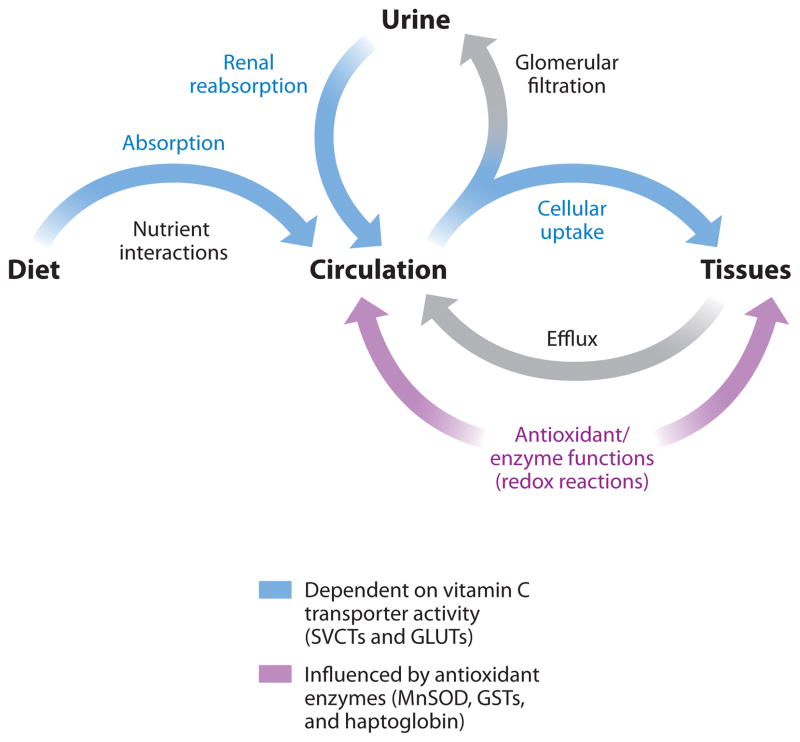
Figure 1.
Vitamin C homeostasis. Vitamin C levels in the circulation and tissues are influenced by several regulatory mechanisms in the body. Proteins involved in vitamin C homeostasis fall under the general-categories transporters (blue) that transport vitamin C across cell membranes and those that modulate oxidative stress (red) and would interact with ascorbate due to its antioxidant properties. GLUT, glucose transporter protein; GST, glutathione S-transferase; MnSOD, manganese superoxide dismutase; SVCT, sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter.