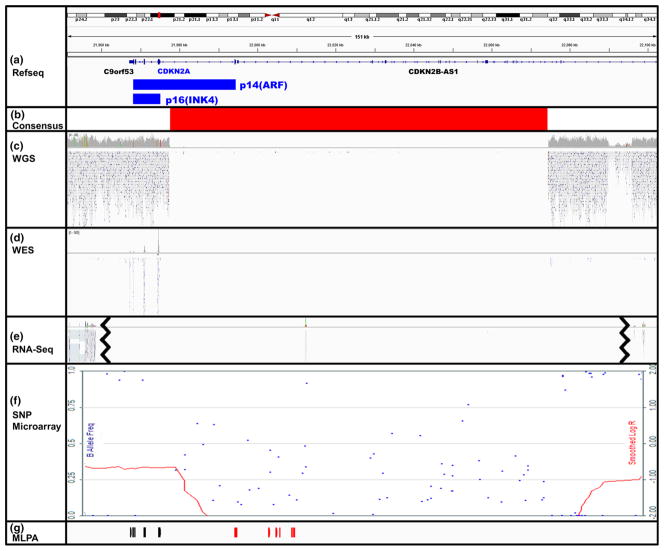
Fig. 3.
CDKN2A/p16 homozygous deletion initially missed by WGS in one case (PA222C). Visualization of WGS reads for p16 gene region (hg19, chr9:21,951,176–22,102,475) in PA222C sample using IGV (Broad Institute, version 2.3.31) and Karyostudio (Illumina, version 1.4). The 2 protein isoforms of p16 (p14(ARF) and p16(INK4), blue) are shown as well as the adjacent genes, C9orf53 and CDKN2B-AS1 (a). There is clear agreement across the methods for the consensus 97 kb homozygous deletion boundaries (b). The homozygous deletion of p16 was not called by the standard Illumina pipeline for WGS data, despite a clear confirmation of the 5′ deletion by visual inspection, due to reference transcript choice (c). The homozygous deletion was detected by WES, as evidenced by the lack of reads (d). RNA-Seq produced no high quality reads that mapped to this deleted region, but there were reads upstream (MTAP) and downstream (DMRTA1) of the homozygous deletion (e line break indicates upstream or downstream reads shows). High density SNP microarray detected the homozygous deletion (red LogR line drops to −2.00 and scattered B allele frequencies) and the flanking LOH regions (red LogR line at −1.00 and B allele frequencies at 0 or 1) (f). MLPA probes were used to confirm the upstream LOH (black) and homozygous deletion (red) regions (g)