Figure 1.
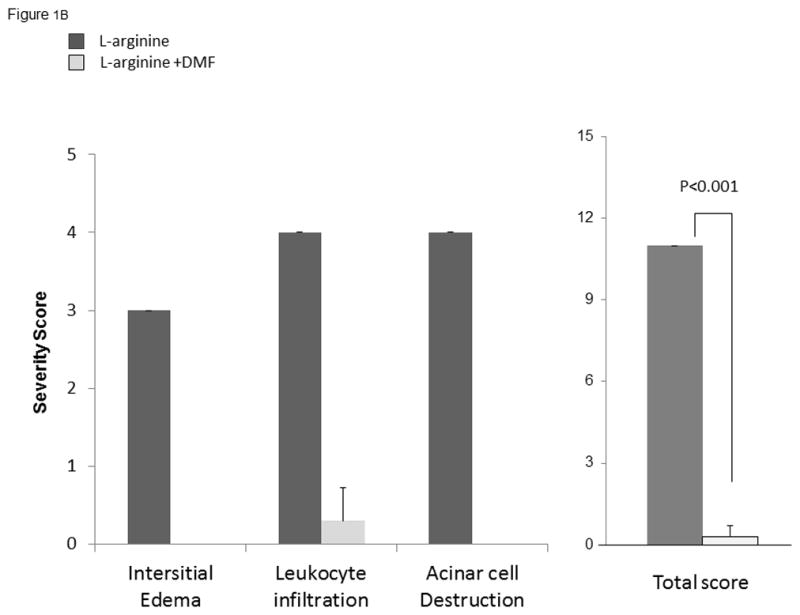
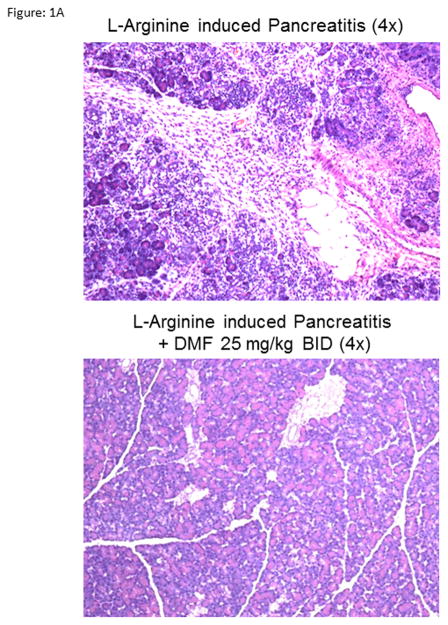
Figure 1A: Histology of L-arginine induced pancreatitis.
Representative photomicrograph of rat pancreatic H&E stained sections. DMF supplementation in rats significantly reduced pancreatic infiltration of inflammatory mediators, destruction of normal acinar architecture, perilobular edema, necrosis of cells and surrounding fat in a rodent model of pancreatitis induced by L-arginine.
Figure 1B: Quantitative pancreatitis score: interstitial edema, leukocyte infiltration, acinar cell destruction
Pancreas histology slides were evaluated by two blinded pathologists and given a score based on severity from 0–3 based on three criteria: edema, infiltration, and acinar cell destruction. Based on quantitative scores for all three criteria there was a significantly higher score for L-arginine compared to L-arginine + DMF (p < 0.001).