Figure 1.
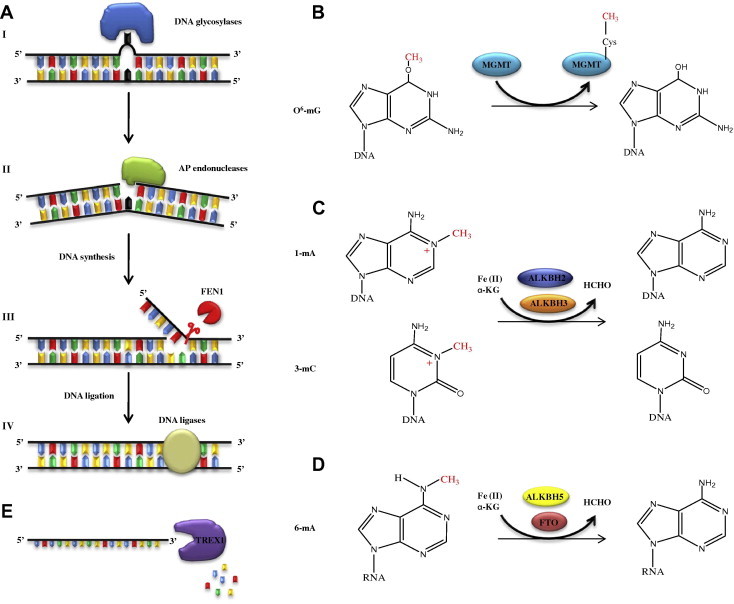
Overview of mechanistic models for enzymatic reactions A. (I) DNA glycosylases catalyze the cleavage of base-sugar bonds; (II) AP endonucleases incise double-stranded DNA at base-free sugar-phosphate residues; (III) FEN1 removes overhangs and flaps from DNA and (IV) eukaryotic DNA ligases ligate DNA ends. B. O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) transfers irreversibly a promutagenic methyl group from alkylated DNA to a specific cysteine residue in the transferase itself. C. DNA dioxygenases remove certain cytotoxic methyl groups from alkylated base residues by oxidative demethylation in the presence of iron and oxoglutarate. D. FTO and ALKBH5 demethylate RNA m6A as a novel epigenetic marker in α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and Fe2+-dependent manner. E. TREX1 is a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease with preference for single-stranded DNA.
