Figure 2.
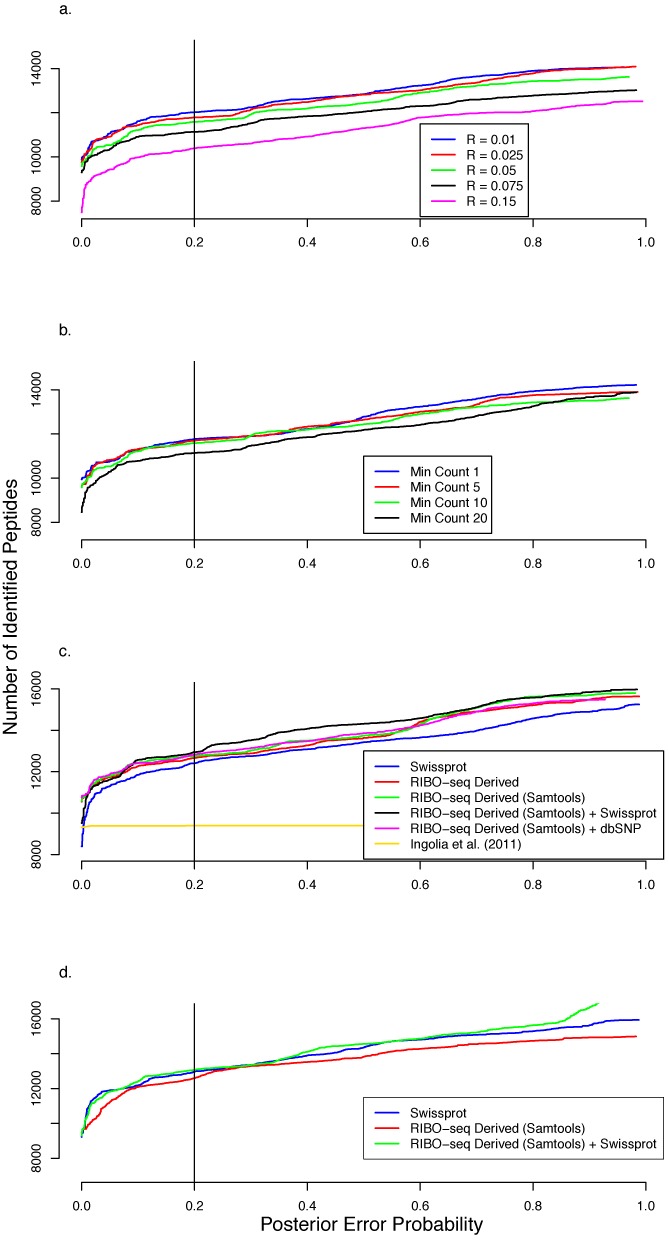
PEP distributions of the number of identified tryptic peptides from shotgun proteome analyses. The searches were performed on a database holding a non-redundant set of tryptic peptides based on the RIBO-seq-derived sequences having annotated TIS (aTIS). These plots demonstrate the impact of the database creation parameters of PROTEOFORMER on downstream MS/MS identification. The cumulative number of peptides identified is plotted on the y-axis and the corresponding PEP (i.e. the probability that a peptide-to-spectrum match is a chance event) is plotted on the x-axis. (a) mESC shotgun data: The effect of changing the RLTM/HARR – RCHX in the TIS calling procedure on the number of tryptic peptides identified with ‘minimum profile count’ (TIS calling) set to 10. The number of identified tryptic peptides decreases with increasing RLTM/HARR – RCHX value. There is a marked increase in the number of highly confident matches (for PEP < 0.2) at lower values of RLTM/HARR – RCHX. (b) mESC shotgun data: The effect of ‘minimum profile count’ on the number of identified tryptic peptides at constant RLTM/HARR – RCHX of 0.01. The number of highly confident identifications decreases with increasing number of ‘minimum profile count’. At a confidence of about 80% (PEP < 0.2) the number of identified peptides is about the same for ‘minimum profile count’ 1 and 5. (c) mESC shotgun data: Comparison of the peptide identification numbers using different database versions. From the PEP distributions it is clear that searches using the RIBO-seq-derived database outperformed those using solely Swiss-Prot. With SNP information (RIBO-seq (SAMtools)) included, the number of identification increases even more, with the best result obtained using a search space combining RIBO-seq-derived sequences (SNP information inclusive) and Swiss-Prot entries at an 80% confidence validation threshold. It is also clear that the rule-based algorithm outperformed the SVM-algorithm applied in Ingolia et al. (8). (d) HCT116 shotgun data: The number of peptide identifications using only RIBO-seq-derived sequences as a search space is lower than searching Swiss-Prot. Yet a significant increase is notable when searching against a combined database (RIBO-seq derived + Swiss-Prot).
