Figure 1.
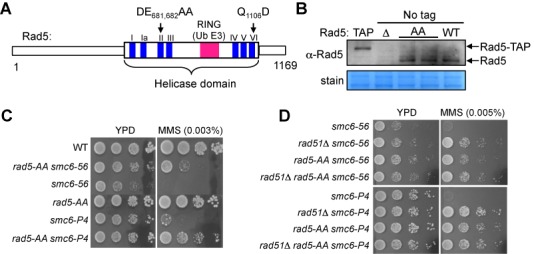
Disruption of the Rad5 Walker B motif suppresses MMS sensitivity of smc6 mutants. (A) Schematic of Rad5 highlights the seven consensus motifs of the helicase domain (blue) as well as the RING ubiquitin E3 domain (pink), which is embedded in the helicase domain. Mutations in the conserved Walker B motif (DE681, 682AA) and conserved motif VI (Q1106D) are indicated. (B) Mutation of the Walker B motif does not affect Rad5 protein levels. Whole cell lysates from wild-type (WT) strains and strains containing TAP-tagged Rad5 (TAP), a RAD5 deletion (Δ) and the Rad5 Walker B mutation (AA) were examined by immunoblotting using an anti-Rad5 antibody (top, Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Bands corresponding to Rad5 and TAP-tagged Rad5 are marked. Equal loading was confirmed by amido black staining (bottom). (C) Mutation of the Walker B motif leads to suppression of the MMS sensitivities of two smc6 mutants (smc6-P4 and smc6–56). 10-fold serial dilutions of exponentially growing cultures of the indicated strains were spotted onto normal media (YPD) and media containing the indicated concentration of MMS. (D)rad5-AA and rad51Δ suppress the MMS sensitivities of smc6 mutants to a similar degree and show epistatic relationships. Experiments were done as in (C).
