Figure 3.
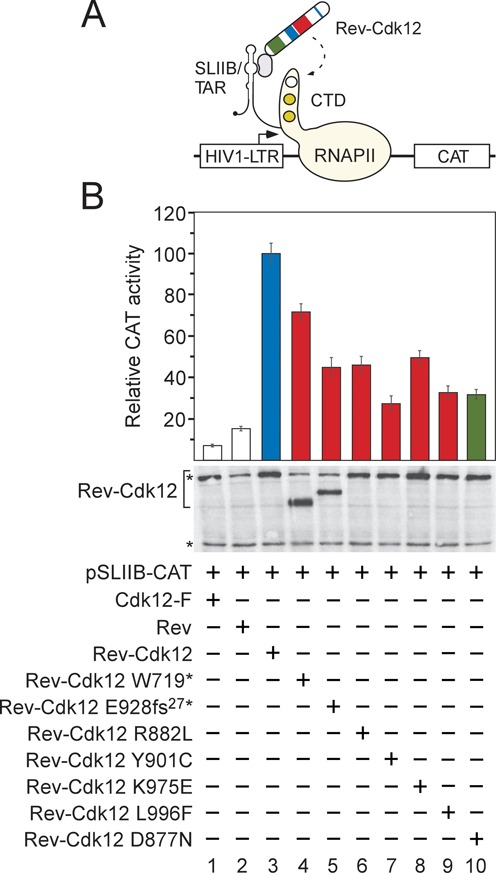
CDK12 mutations in HGS-OvCa decrease transcriptional activation by Cdk12. (A) Schematic depiction of the heterologous RNA tethering assay. Plasmid reporter pSLIIB-CAT contains modified HIV1-LTR promoter in which the apical region of transactivation response RNA element (TAR) was substituted with 29-nucleotide stem-loop IIB (SLIIB) subdomain of the HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE), the Rev binding RNA sequence. The interaction between Rev (pink oval) and SLIIB within the TAR/SLIIB stem-loop structure at the 5′ end of nascent RNA tethers the Rev-Cdk12 chimeric protein to RNAPII engaged in transcription, resulting in elevated transcription of CAT reporter gene. CTD of the biggest RNAPII subunit Rbp1 is represented as a tail of RNAPII (yellow), wherein white circle depicts Ser2 residue to be phosphorylated by Rev-Cdk12 (dashed arrow) and gold circles depict Ser5 and Ser7 residues in an already phosphorylated form. Arrow within HIV1-LTR indicates transcription start site. (B) CDK12 HGS-OvCa mutations compromise stimulation of transcription by Rev-Cdk12. HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with pSLIIB-CAT reporter gene and plasmids encoding the proteins indicated below the graph. Transcriptional activities of Cdk12-F (white bar 1), Rev (white bar 2), the mutant Rev-Cdk12 chimeras (red bars) and catalytically dead Rev-Cdk12 D887N chimera (green bar) are represented as CAT activities relative to the activity of wild-type Rev-Cdk12 chimera (blue bar), which was set to 100%. Results are presented as the mean ± SD. Levels of the Rev-Cdk12 chimeras and endogenous Cdk12 protein are shown below the graph and were detected by Western blotting using Cdk12 antibody. The top asterisk (*) indicates migration of the endogenous Cdk12 protein and the bottom one indicates the position of an unspecific band recognized by the Cdk12 antibody, which serves as a loading control.
