Figure 6.
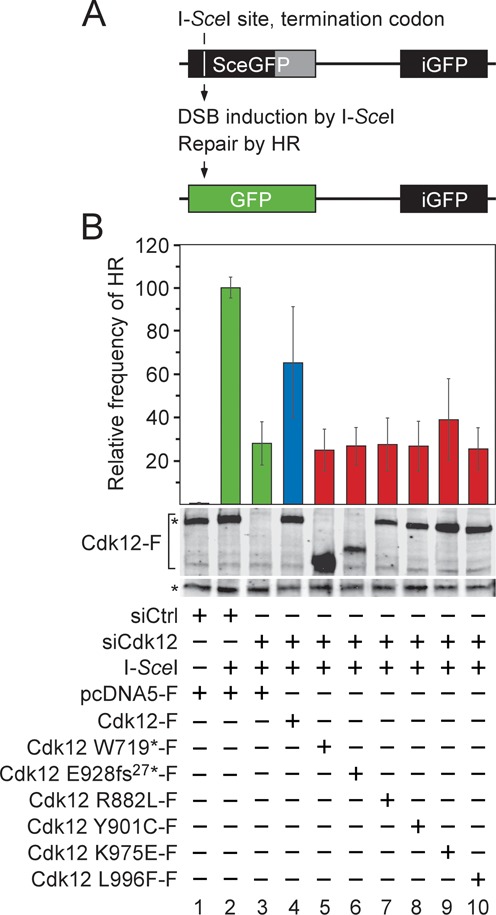
CDK12 mutations in HGS-OvCa abrogate the ability of Cdk12/CycK to stimulate the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by HR. (A) Schematic representation of the DR-GFP recombination substrate. The defective EGFP genes of the cassette, separated by 3.7 kb, are shown (top). The first one (SceGFP) contains an I-SceI endonuclease site and an in-frame termination codon (white vertical line), while the second one (iGFP) is an internal EGFP fragment, yielding GFP− cells. The homologous EGFP sequences are depicted as black rectangles and the non-repetitive EGFP sequence is depicted as gray rectangle. Induction of DSB by I-SceI triggers the repair of SceGFP by HR using the iGFP sequence as a donor DNA, resulting in wild-type EGFP (green rectangle) and GFP+ cells (bottom). (B) The mutant Cdk12 proteins fail to promote the repair of the DSB by HR. HeLa DR-GFP cells were treated with the control or Cdk12 #2 siRNA and transfected with the I-SceI expression plasmid together with plasmids encoding the wild-type (blue bar) or mutant (red bars) Cdk12-F proteins as indicated below the graph. The HR frequency for each experimental condition is represented as the frequency relative to the one reached by the I-SceI expression in the control siRNA-treated cells, which was set to 100% (green bar). Results are presented as the mean ± SD. Levels of the endogenous Cdk12 and Cdk12-F proteins are shown below the graph and were detected by Western blotting using Cdk12 antibody. The top asterisk (*) indicates migration of the endogenous Cdk12 protein and the bottom one indicates the position of an unspecific band recognized by the Cdk12 antibody, which serves as a loading control.
