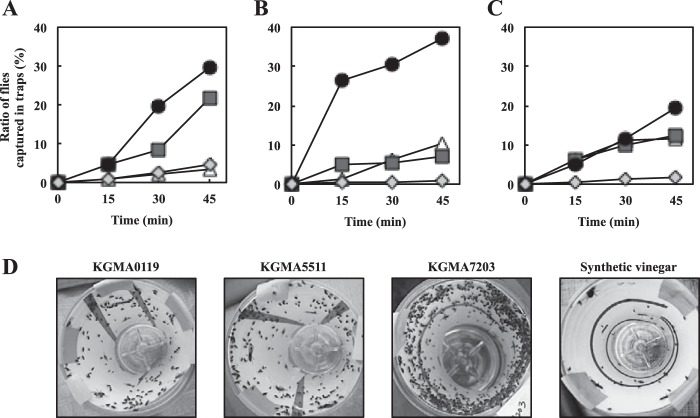
FIG 6.
The fly-trapping experiments with culture supernatants from various strains. Strains KGMA0119 (wild type), KGMA5511 (ΔpyrE ΔilvC::pyrE), and KGMA7203 [ΔpyrE KelrpΔ(397-511)::pyrE] were cultured in YPD broth supplemented with 1.0% sodium l-lactate (and 12 mM BCAAs for KGMA5511). After culture for 34 h, cell-free supernatants were prepared and used for fly-trapping experiments. (A to C) Attractiveness of the supernatants to fruit flies. The attractiveness of the supernatants was indicated as a ratio of flies captured in traps to the total fly population released (%). The synthetic vinegar was composed of 0.7% acetic acid, 0.13% acetoin, and 0.007% isobutyric acid. The trapping experiments were conducted in triplicate. The first (A), second (B), and third (C) trials were conducted in the sunny afternoon (30°C), in the cloudy morning (28°C), and in the cloudy afternoon (28°C), respectively. See Materials and Methods for more-detailed conditions during the experiments (date and time). White triangles, KGMA0119; dark gray squares, KGMA5511; black circles, KGMA7203; light gray diamonds, synthetic vinegar. (D) Flies captured in traps. The results are consistent with the data of 45 min in panel B.