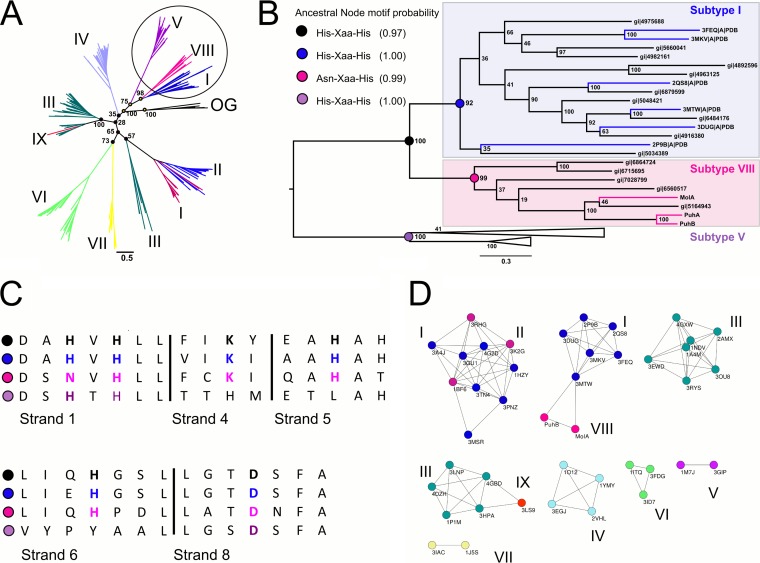
FIG 8.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the nine current subtypes in the AHS. The three subtypes used for ancestral reconstruction and relevant bootstrap values are highlighted. (OG, outgroup) (B) The subtree used to determine the ancestral sequences of subtype VIII and I members. Reconstruction of the metal-binding motif in the ancestor of subtype VIII and I members (black node) provides evidence that this ancestor was binuclear Colored branches indicate characterized enzymes. (C) Sequence alignment of the four ancestral nodes showing the conservation of the metal-coordinating residues. (D) SSNs of structurally characterized AHS enzymes. Each node represents a single sequence, and each edge represents a connection between two sequences with a BLAST E value of >1 × E−20. The subtypes are color coded, and the PDB codes of the enzymes are shown.