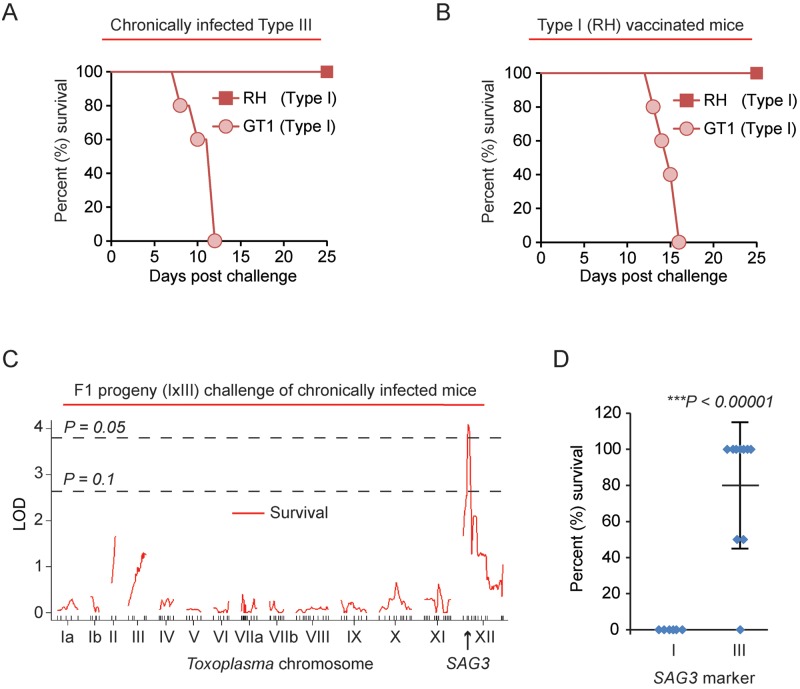
FIG 4 .
The T. gondii type I ROP5/SAG3 locus is correlated with lethal secondary infection. (A) Type III (CEP) chronically infected C57BL/6 mice (day 37 of chronic infection) were challenged with 5 × 104 tachyzoites of either the RH (n = 2) or GT1 (n = 5) type I strains; cumulative survival is plotted. (B) C57BL/6 mice were vaccinated with 106 tachyzoites of the uracil auxotroph type I RH Δku80 Δompdc Δup vaccine strain (83), and 34 days later mice were challenged with either 5 × 104 tachyzoites of the type I RH (n = 4) strain or 5 × 103 tachyzoites of the type I GT1 strain (n = 5). Cumulative survival is plotted. (C) Type III chronically infected C57BL/6 mice (day 34 of chronic infection) were challenged with 5 × 104 tachyzoites of 16 different F1 progeny derived from a cross between the GT1 (type I) and CTG (type III) strains. The chosen progeny have the type I CS6 marker on Toxoplasma chromosome VIIa, a marker which detects an informative SNP in the ROP18 allele; thus, these F1 progeny express ROP18 and are 100% lethal in naive mice (34). The running LOD score for each of the 176 markers on the various Toxoplasma chromosomes and mouse survival (%) at 26 days after challenge is plotted (red line). The SAG3 marker on Toxoplasma chromosome XII returned the highest LOD score (4.1; P < 0.05). Significance was estimated based on 1,000 permutations at each marker; thresholds of P = 0.05 and P = 0.1 are shown. (D) Effects of the type I and type III SAG3 locus on mouse survival at 26 days. *, significant P value based on Student’s t test.