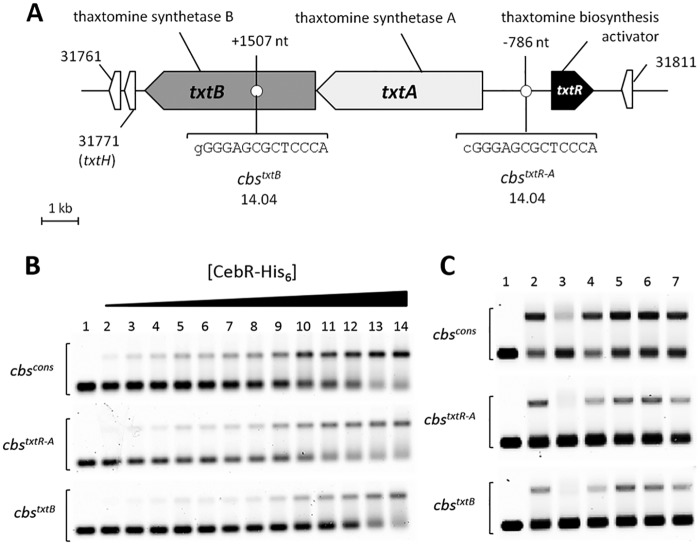
FIG 1 .
CebR binding to cbs associated with thaxtomin biosynthetic genes is relieved by cellobiose. (A) Sequences and positions of CebR-binding sites identified in the chromosome region of the thaxtomin biosynthetic genes in S. scabies. Numbers associated with genes/ORFs are SCAB numbers from the annotated genome of S. scabies 87-22. The lowercase letters indicate nucleotides that do not match with the cbs consensus sequence. (B) EMSA demonstrating CebR binding to DNA motifs identified in the txtRA intergenic region (cbstxtR-A) and in txtB (cbstxtB). Numbers 1 to 14 refer to increasing concentrations of pure CebR-His6, i.e., 0 (free probe, 30 nM), 80, 160, 240, 320, 400, 480, 560, 640, 720, 960, 1,200, 1,600, and 3,200 nM, respectively. (C) EMSAs demonstrating cellobiose as the best allosteric effector of CebR. Numbers 1 and 2 refer to EMSAs with free probes (6 nM) and with probes incubated with CebR-His6, respectively. Numbers 3 to 7 refer to EMSAs with CebR-His6 preincubated with oligosaccharides, i.e., cellobiose (lane 3), cellotriose (lane 4), cellotetraose (lane 5), cellopentaose (lane 6), or cellohexaose (lane 7). Quantification of the shifted bands revealed that cellobiose (lane 3), cellotriose (lane 4), and cellohexaose (lane 7) were able to impair the CebR DNA-binding ability by approximately 56, 20, and 12%, respectively.