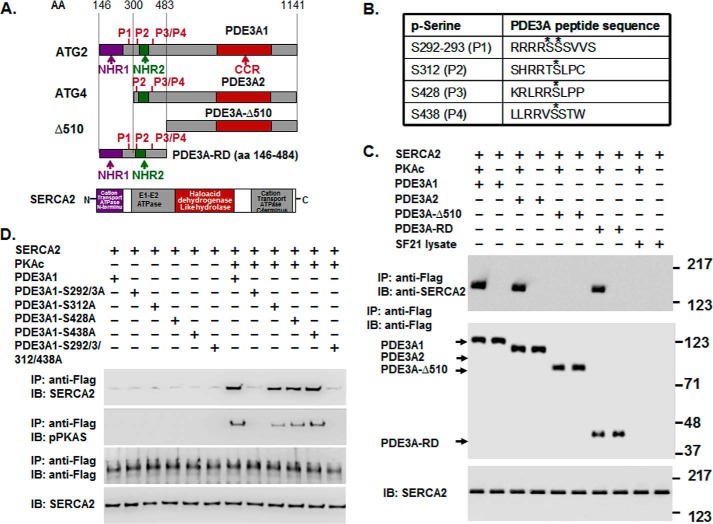
FIGURE 6.
rPKAc phosphorylates rhPDE3A and increases its interactions with rSERCA2. A, schemes representing protein domains and phosphorylation sites in FLAG-tagged-PDE3A isoforms (NHR1, transmembrane domain (obligatory membrane insertion domain); NHR2, membrane association domain; CCR, conserved C-terminal catalytic region; P1–4, predicted PKA phosphorylation sites; rhPDE3A and truncated mutants (PDE3A2, PDE3A-Δ510, PDE3A-RD (regulatory domain: aa 146–484)) and protein domains in rSERCA2 (1042 amino acids, including 3–77 cation transporter N termini; 93–341, E1-E2 ATPase; 345–724, haloacid dehydrogenase like hydrolase; 819–991, cation transporter ATPase C terminus). B, putative PKA phosphorylation sites in PDE3A designated with asterisks. C and D, purified rSERCA2 (150 ng) (Abnova) and 50 units of FLAG-tagged rhPDE3A1 or FLAG-tagged truncated mutants ((rhPDE3A2, rhPDE3A-Δ510, and rhPDE3A-RD) (C) or FLAG-tagged mutants lacking the PKA putative phosphorylation sites of rhPDE3A1 (S292A/S293A (P1), S312A (P2), S428A (P3), S438A (P4), S292A/S293A/S312A/S438A (P5)) (D) were incubated for 30 min at 30 °C in phosphorylation buffer containing 5 mm MgCl2 and 200 μm ATP in the presence or absence of rPKAc. As described under “Methods,” proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG M2 magnetic beads. Immunoprecipitated proteins bound to the anti-FLAG-M2 magnetic beads were eluted by boiling in Laemmli SDS buffer (200 μl), and samples (15–20 μl) of eluted proteins as well as of reaction mixtures (lowest panel) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting (IB) as indicated with anti-SERCA2, anti-PKA substrate, and anti-FLAG-HRP primary antibodies and anti-mouse-HRP or anti-rabbit-HRP secondary antibodies as needed. Lowest panels, input control (SERCA2). Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments.