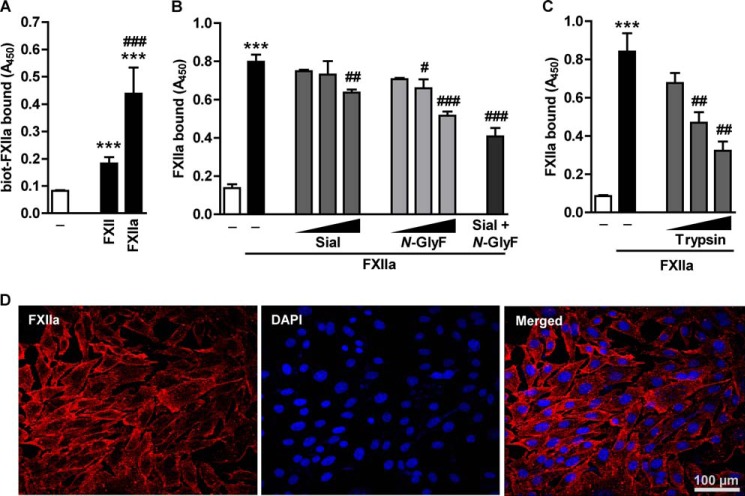
FIGURE 1.
Glycosidases and proteases affect FXIIa binding to the HLF surface. A, HLF were treated with 1 μg/ml biotin-labeled FXII/FXIIa for 1 h at 37 °C. Following the incubation with peroxidase-labeled streptavidin, binding of FXII/FXIIa to the cell surface was analyzed. Data represent mean ± S.D. (n = 4); ***, p < 0.001 versus control; ###, p < 0.001 versus FXII. B, cells were treated with 1, 0.1, or 0.01 units/ml sialidase (Sial), N-Glycosidase F (N-GlyF), or a combination of both enzymes (0.1 units/ml each) for 60 min at 37 °C to remove surface GAG. C, to digest surface proteins, cells were incubated with 0.00025, 0.0001, or 0.00005% (w/v) trypsin for 3 min at 37 °C. B and C, after enzyme removal, cells were incubated with 2.75 μg/ml FXIIa and subjected to cell-based ELISA with anti-FXII antibodies to determine the degree of FXIIa accumulation on the cell surface. Data represent mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 4); ***, p < 0.001 versus control; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 versus FXIIa only. D, representative immunofluorescence pictures demonstrating binding of Alexa Fluor® 546-labeled FXIIa to HLF. Magnification was ×630.