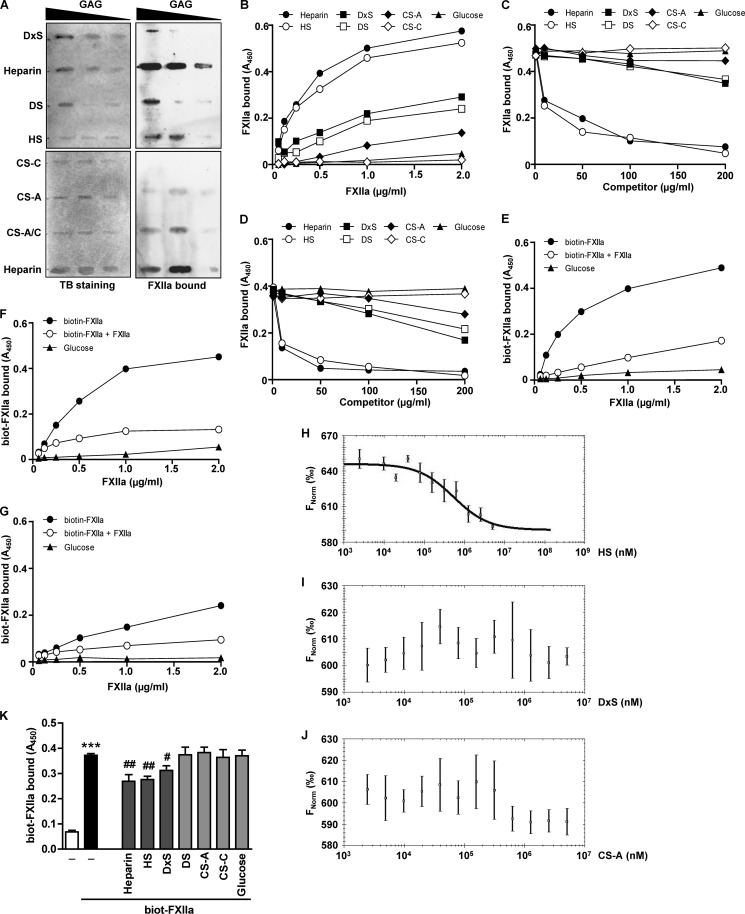
FIGURE 4.
FXIIa binds to immobilized and cell surface-associated HS. A, binding of FXIIa to DxS or DS (30, 20 or 10 μg of each), heparin or HS (10, 5, or 2.5 μg of each), and CS-A, CS-C, or CS-A/C (40, 20, or 10 μg of each) immobilized on a nylon membrane. Toluidine blue (TB) staining and immunodetection with anti-FXII antibodies were used to visualize immobilized GAGs and bound FXIIa, respectively. The membranes shown are representative of six independent experiments. B–D, FXIIa binding to GAGs immobilized onto the surface of microtiter plates. B, heparin, HS, DxS, DS, or glucose (25 μg/ml each) and CS-A or CS-C (250 μg/ml each) were surface-immobilized and incubated with the indicated amounts of FXIIa. C and D, surface-immobilized HS (C) or DS (D) was incubated with 2 μg/ml FXIIa in the presence of the indicated amounts of heparin, HS, DxS, DS, CS-A, CS-C, or glucose used as competitors. E–G, surface-immobilized HS (E), heparin (F), or DS (G) was incubated with increasing amounts of biotinylated FXIIa in the presence or absence of a 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled FXIIa acting as a competitor. Following the washing steps, bound FXIIa was quantified using anti-FXII antibody (B–D) or directly with peroxidase-coupled streptavidin (E–G). B–G, data are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. H–J, binding of FXIIa to HS (H), DxS (I), or CS-A (J) as assessed by microscale thermophoresis. KD values were calculated from three independent thermophoresis measurements. K, effect of solubilized GAG on the FXIIa binding to HLF. Biotinylated FXIIa was incubated with HLF in the absence or presence of 100 μg/ml heparin, HS, DxS, DS, or glucose or 200 μg/ml CS-A or CS-C. After extensive washing steps to remove unbound FXIIa and competitors, the amount of cell surface bound FXIIa was quantified using peroxidase-coupled streptavidin. Data represent mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 4); ***, p < 0.001 versus control; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01 versus FXIIa only.