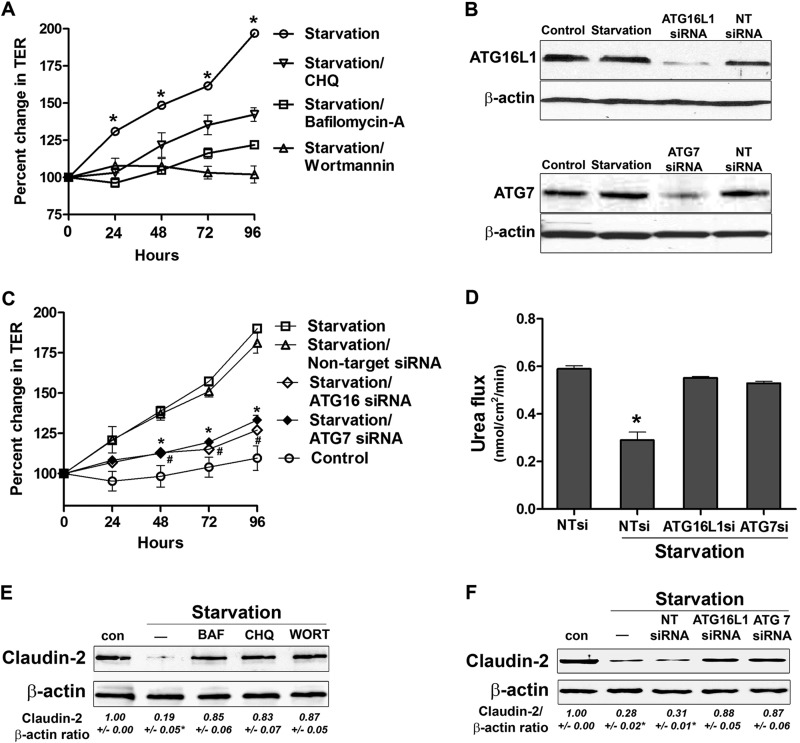
FIGURE 6.
Autophagy inhibition attenuates the starvation-induced enhancement in the TJ barrier. A, incubation of Caco-2 cells in starvation medium with bafilomycin A (20 nm), chloroquine (CHQ, 20 μm), and wortmannin (200 nm) significantly inhibited the increase in TER caused by starvation. *, p < 0.01 versus all other groups. B, the respective siRNA transfection, but not NT siRNA transfection, produced a significant knockdown of ATG16L1 and ATG7 protein expression. C, inhibition of the autophagy-related proteins ATG16L1 and ATG7 with siRNA transfection, but not non-target siRNA transfection, significantly inhibited the increase in TER caused by starvation. * and #, p < 0.01 versus starvation. D, ATG 16L1 and ATG7 siRNA, but not non-target siRNA transfection, significantly attenuated the starvation-induced reduction in paracellular flux of urea (96 h of starvation). *, p < 0.01 versus all other groups. E and F, autophagy inhibition during starvation by bafilomycin A (BAF), chloroquine, and wortmannin (WORT) (E) and ATG16L1 and ATG7 siRNA (F) prevented a starvation-induced reduction in claudin-2 protein level. β-actin is shown as a loading control (con). The blots represent at least three independent experiments. The claudin-2:actin ratio represents the densitometry analysis. *, p < 0.01 versus all other groups.