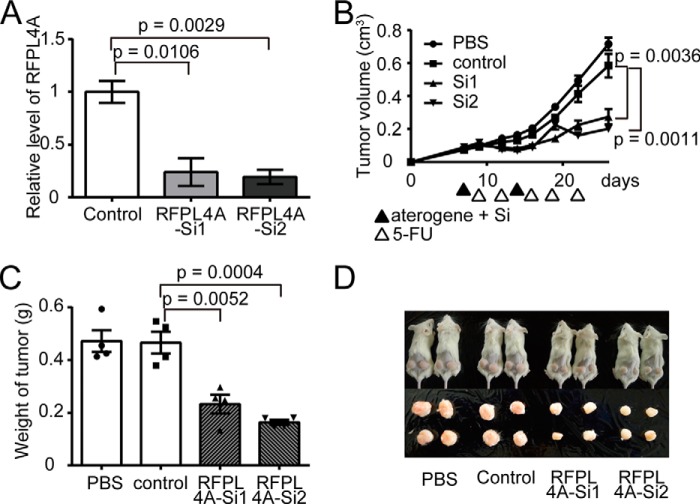
FIGURE 8.
RNAi-based inhibition of RFPL4A increased the sensitivity of HCT116 to chemotherapy in vivo. A, decreased expression of RFPL4A in HCT116 cells treated with siRNAs targeting RFPL4A (assessed by qPCR). Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments (n = 3). B, in vivo siRNA treatment of HCT116 tumors. Control HCT116 cells (5 × 106) were implanted in NOD/SCID mice and, on days 7 and 14, were treated with PBS, scrambled control siRNA plus atelocollagen, or two siRNAs (Si1 and Si2) against RFPL4A plus atelocollagen. NOD/SCID mice were administered intraperitoneal injection of 5-FU (30 mg/kg) at days 9, 12, 16, 19, and 22. Data represent the mean tumor volumes, calculated using the formula, (longest diameter) × (shortest diameter)2 × 0.5. The statistical significance of the difference between the control and RFPL4A-expressing HCT116 cells was determined by two-way ANOVA. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of four individual experiments (n = 4 for each). C, comparison of the tumor weights after treatment with atelocollagen and 5-FU at 26 days. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of four independent experiments (n = 4 for each). D, images of tumors excised on day 35.