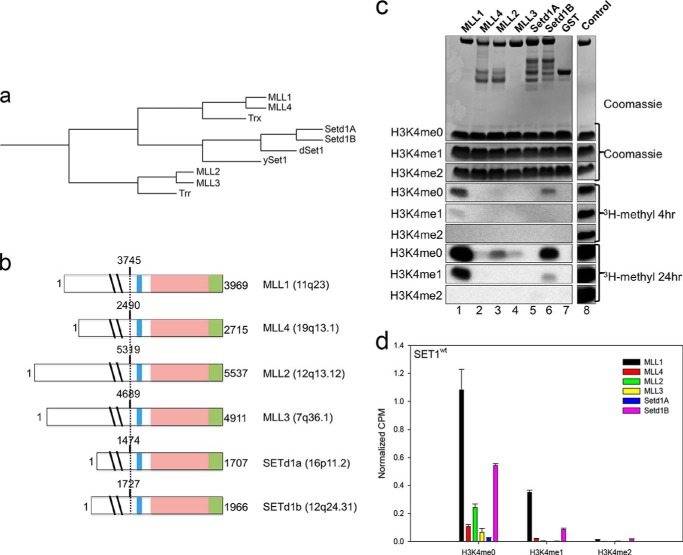
FIGURE 1.
Human SET1 family members predominantly catalyze monomethylation of H3K4. a, phylogenetic cluster analysis (Clustal Omega (66)) of SET1 family members using full-length protein sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ySet1), Drosophila (dSet1, Trx, and Trr), and humans (MLL1–4, SETd1A/B). b, schematic representation of full-length human SET1 family proteins. The catalytic SET domain is shown in light pink; the post-SET region is shown in green, and the WDR5 interaction (Win) motif is shown in blue. Dotted lines represent the N terminus of the recombinant constructs used in this study, beginning with the residues noted above each construct. c, comparison of histone methyltransferase activity among human SET1 family SET domains. Upper panels show Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gels, and the lower panels shows [3H]methyl incorporation by fluorography after a 4-h exposure (middle panels), and after a 24-h exposure (lowest panels). The control lane shows the activity of the MLL1 SET domain on 100 μm unmodified H3 peptide, which is included on each gel. The control lanes are from the same gel at the same exposure but were cropped for clarity. d, quantification of radioactivity from excised histone H3 bands by LSC. Data are normalized to the activity level of the control lane on each gel. Error bars represent the S.E. of measurement between three independent experiments.