FIGURE 3.
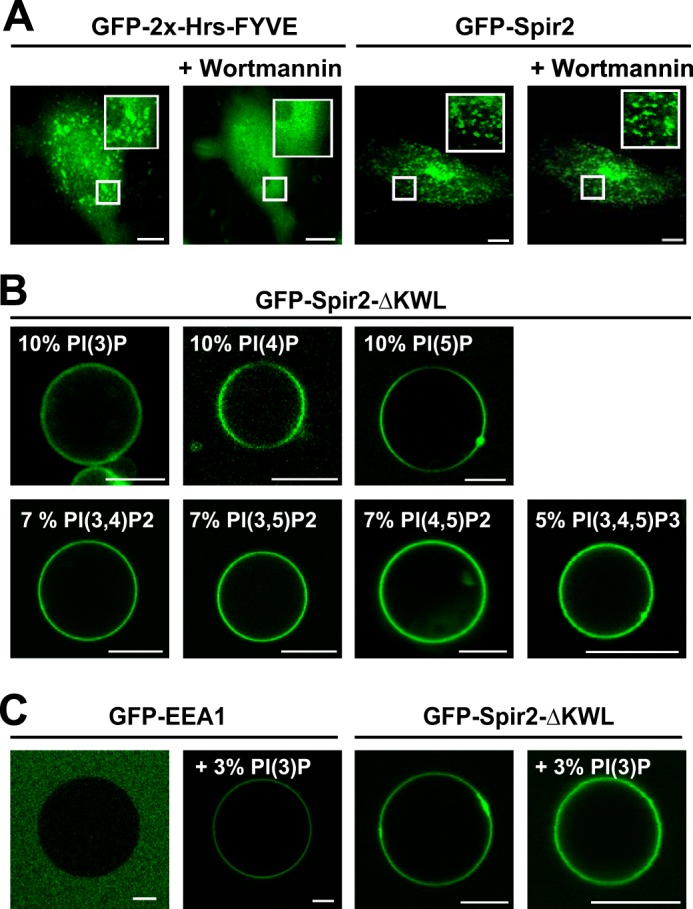
Promiscuous interaction of Spir-2 with phosphoinositides. A, confocal images showing the subcellular distribution of the canonical Hrs FYVE domain (GFP-2x-Hrs-FYVE; mouse Hrs, aa 147–223) and the Spir-2 FYVE-type domain (GFP-Spir-2) in HeLa cells in the presence and absence of 200 nm PI(3)P kinase inhibitor wortmannin. Under wortmannin, Spir-2 remains membrane-associated. B, nonspecific binding of GFP-Spir-2-ΔKWL to GUVs composed of DOPC and different PIP species. C, PI(3)P-specific binding of the classical FYVE domain GFP-EEA1 (human EEA1, aa 1277–1411) and nonspecific binding of GFP-Spir-2-ΔKWL to GUVs composed of 50% 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC), 20% 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE), 20% cholesterol, and 10% 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylserine (POPS) ± 3% PI(3)P. Scale bars represent 10 μm.
