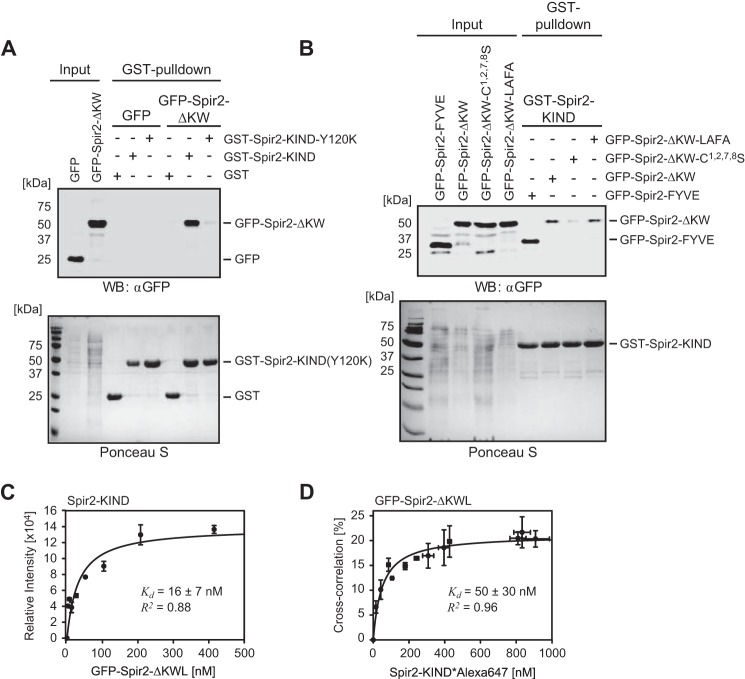
FIGURE 5.
Spir-2 C-terminal FYVE-type domain strongly binds N-terminal KIND in solution. A and B, GST pulldown experiments using GST-tagged Spir-2-KIND as a bait to probe mutual interactions with GFP-tagged C-terminal Spir-2 proteins (Input) transiently expressed in HEK 293 cells. The cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting (anti-GFP) and Ponceau S staining to document the protein content. A, the C-terminal fragment (GFP-Spir-2-ΔKW) shows strong interactions with the N-terminal fragment (GST-Spir-2-KIND) but not a dysfunctional KIND mutant (GST-Spir-2-KIND-Y120K) (experimental repeats, n = 4). B, a functional FYVE-type domain (GFP-Spir-2-ΔKW and GFP-Spir-2-FYVE) is sufficient for binding of GST-Spir-2-KIND. Mutations in the turret loop had little effect (LAFA mutant), whereas cysteine replacements impaired binding (n = 3). C and D, binding studies using purified recombinant Spir-2 fragments. C, titration of GFP-Spir-2-ΔKWL to quantify binding of non-tagged Spir-2-KIND analyzed by EIA. Progressive binding (average ECL signal) was evaluated by assuming a single binding site. D, complementary binding assay in homogenous solution. Titration of fluorescently labeled Spir-2-KIND*Alexa647 was carried out with constant amounts of GFP-Spir-2-ΔKWL (25 nm). The fraction that was ligand-bound was quantified by FCCS. Evaluation of the curve assumes a 1:1 binding stoichiometry (39). Error bars represent S.D. (n = 3). WB, Western blotting.