FIGURE 2.
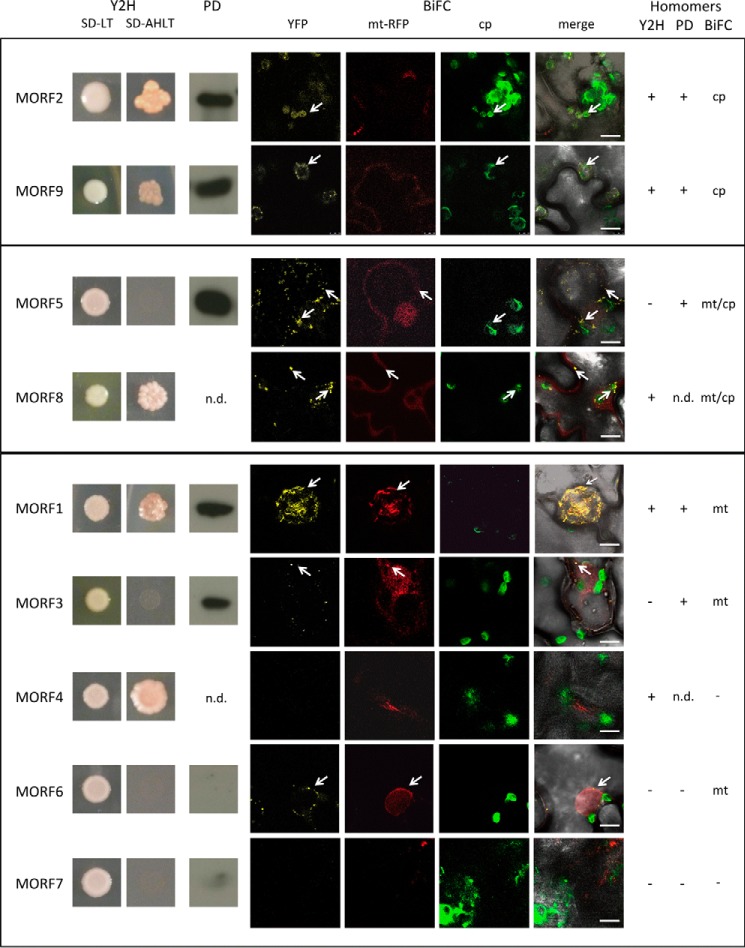
Most MORF proteins can connect to homomers. The plastid-located MORF2 and MORF9 proteins form homomers in Y2H assays, in pulldown probings, and in BiFC experiments. The results of the Y2H analyses are shown in the left panels (Y2H), with SD-LT showing colony growth and SD-AHLT showing growth only upon MORF-MORF interaction on the selective medium lacking adenine and histidine. Pulldown probing results (PD) show the respective chemiluminescence signal after detection with an anti-GFP antibody (n.d. = not determined). The BiFC assays (BiFC) are displayed with YFP showing the interaction detecting fluorescence, mt-RFP showing the mitochondrial fluorescences, and cp showing the chloroplast fluorescences. These are laid over the bright field image in the merge panels. The dual-targeted MORF8 protein shows homomer interaction signals in the Y2H assays as well as in mitochondria and chloroplasts in the BiFC experiments. In addition, the dual-targeted MORF5 protein does not activate the yeast promoter through homomer interaction, but connects in the pulldown assays and yields a reconstituted BiFC fluorescence in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Of the mitochondrial MORF proteins, MORF1 shows strong homomer interaction in the Y2H as well as in the pulldown assays and BiFC experiments. MORF3 shows homomer interactions in the pulldown and in the BiFC assays. Of the other mitochondrial MORF proteins, only MORF4 undergoes a homomer interaction in the Y2H system, which is not seen in the BiFC experiments. The MORF6 protein yields a weak YFP signal in mitochondria, and MORF7 does not show homomer formation in any assay. Results of the three assay systems are summarized on the right. n.d. = not determined. Arrows point at samples for better orientation.