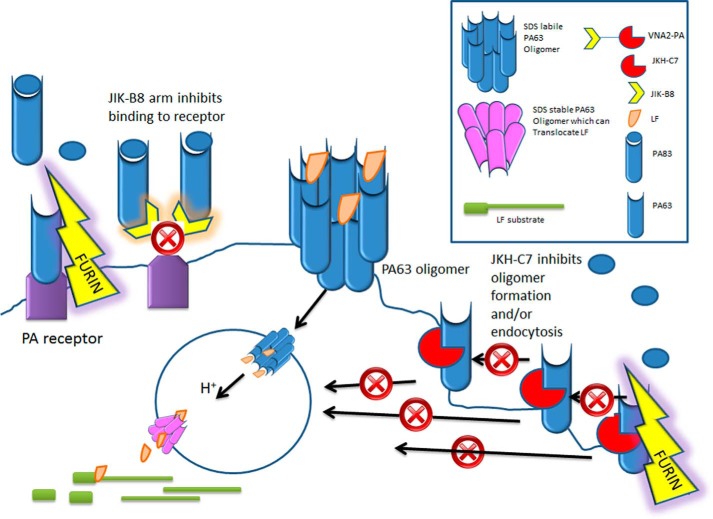
FIGURE 7.
Model for mechanism of action of two VHHs that make up neutralizing VNA2-PA: PA83 normally binds to cellular receptors and is cleaved by cellular furin to form PA63. PA63 monomers immediately oligomerize to form the binding sites for LF. The oligomer complex is endocytosed (with or without LF cargo) and upon arrival in the acidic endosomal environment alters in conformation to form a pore through which LF can be translocated to the cytosol where it cleaves its substrates. VNA2-PA, which is a heterodimer of JIK-B8 and JKH-C7, inhibits this process through two mechanisms. The JIK-B8 arm binds to the receptor binding domain of PA83 and inhibits binding of the toxin to its receptor. The JKH-C7 arm binds to a conformational epitope on PA83 that does not prevent cleavage of the toxin to PA63 form but prevents oligomerization of PA63 at the cell surface or its endocytosis into the cell.